vue
渐进式 JavaScript 框架
Vue 只关注视图层, 采用自底向上增量开发的设计。
Vue 的目标是通过尽可能简单的 API 实现响应的数据绑定和组合的视图组件。
SOC 关注点分离原则
网络通信: axios
页面跳转:vue-router
状态管理:vuex
Vue-Ui:ICE
vue特点
- 采用组件化模式,提高代码复用率,且让代码好维护。
- 声明式编码,让编码人员无需直接操作DOM,提高开发效率。
- 虚拟Dom+优秀的Diff算法,尽量复用Dom节点。
引入
1 | <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script> |
快速上手
搭建环境
开发者工具
安装
示例
1 |
|
- 想让vue工作,就必须创建一个vue实例,且要传入一个配置对象
- root容器的语法依然符合html语法,只不过混入了一些特殊的vue语法
- root容器的代码被称为(vue模板)
- vue实例与vue模板是一对一的关系
Vue核心
模板语法
html中包含了一些js语法代码
插值
双大括号表示
用于解析标签体内容
1 | <!-- 此示例以下的所有实例都省略hand等元素 --> |
指令
以v-开头
用于解析标签,包括属性、内容、绑定事件等
1 | <body> |
数据绑定
单向绑定
数据只能从data流向页面
1 | <body> |
双向绑定
数据不仅可以从data流向页面,也能从页面流向data
1 | <body> |
v-model:value可以简写为v-model
v-model默认收集的是value
el与data的两种写法
el
第一种
1 | <body> |
第二种
1 | <body> |
data
对象式
1 | <body> |
函数式
1 | <body> |
MVVM
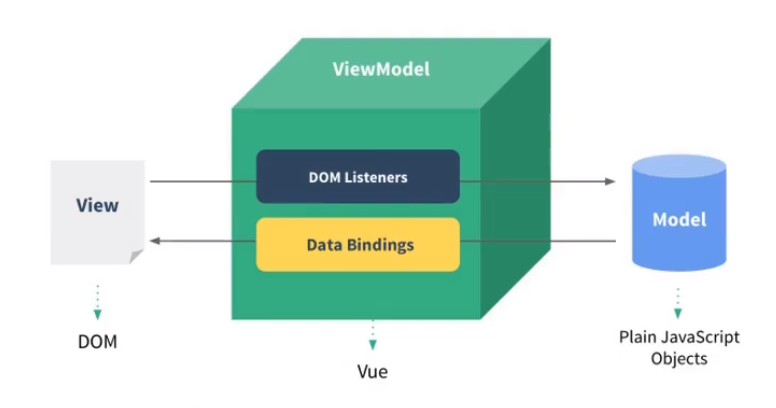
- M 模型:Model,对应data的数据
- V 视图:View,模板
- VM 视图模型 ViewModel,Vue实例对象
虽然没有完全遵循 MVVM 模型,但是 Vue 的设计也受到了它的启发。因此在文档中经常会使用 vm (ViewModel 的缩写) 这个变量名表示 Vue 实例。
事件处理
绑定事件
使用v-on:xx或者@xxx绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名
事件的回调需要配置在methods对象中,最终会在vm上
1 | <body> |
不传参
事件中的this是Vue的vm实例,或者组件的实例对象
1 | <body> |
传参
@click="xxx"与@click="xxx($event)"效果一致 ,但是后者可以传参
1 | <body> |
事件的修饰符
修饰符
| 修饰符可以连续写 | ||
| 例如`` |
示例
1 | * { |
-
1 | <body> |
键盘事件
| 别名 | 内容 | |
|---|---|---|
| enter | 回车 | |
| delete | 删除 | |
| esc | exc | |
| space | space | |
| tab | tab | |
| up | 上 | |
| down | 下 | |
| left | 左 | |
| right | 右 | |
| kebab-case | 未提供别名的按键,可以通关原石key值去绑定(kebab-case) |
- 系统修饰键,ctrl,alt,shift,meta,
- 配合keyup按下ctrl再按其他键,随后释放其他键,事件才会触发
- 配合keydown 正常触发事件
1 | <body> |
计算属性与监视
计算属性
拟定一个需求:两个输入框输入姓名年龄,并且实时在下面展示
插值语法实现
1 | <body> |
methods实现
1 | <body> |
计算属性实现
1 | <body> |
若值只读则可以简写为
1 | <body> |
监视属性
当监视的属性发生变化时,回调函数自动调用
监视属性必须存在,才能进行监视
监视属性的,两种写法
第一种
1 | <body> |
第二种
1 | <body> |
immediate: true,可以在初始化的时候执行监视
深度监视
Vue的watch默认不监视对象内部值的改变(1层)
配置deep:true可以监视对象内部值改变(多层)
监视对象内固定的属性
1 | <body> |
监视整个对象
1 | <body> |
class 与 style 绑定
class绑定
示例用css:
1 | .basic { |
字符串写法
适用于class不确定需要动态指定
1 | <body> |
数组写法
适用于class绑定的名字与个数都不确定
1 | <body> |
对象写法
适用于class绑定的名字与个数均确定,但要动态决定用不用
1 | <body> |
style绑定
字符串写法
1 | <body> |
对象写法
1 | <body> |
对象数组写法
1 | <body> |
条件渲染 (判断)
v-show
1 | <body> |
v-if & v-else
1 |
|
异同
- 异
v-if等会将dom元素动态添加在页面上
v-show的dom元素是一直存在于页面上,通过改变 display来控制元素的显示与隐藏 - 同
都可以控制元素的可见度
参数均为表达式,只要输出布尔值即可示例
通过按钮控制n,从而控制dom元素的可见1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31<body>
<div id="root">
<div>
<span>数字为:{{n}}</span>
<button @click="n++">点我N++</button>
<h1 v-show="n === 1">Hello world v-show-1</h1>
<h1 v-show="n === 2">Hello world v-show-2</h1>
<h1 v-show="n === 3">Hello world v-show-3</h1>
<h1 v-if="n === 1">Hello world v-if-1</h1>
<h1 v-if="n === 1">Hello world v-if-1</h1>
<h1 v-if="n === 2">Hello world v-if-2</h1>
<h1 v-if="n === 3">Hello world v-if-3</h1>
<h1 v-else>Hello world v-else-4</h1>
<h1 v-if="n === 3">Hello world v-if-3</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="n === 4">Hello world v-else-if-4</h1>
</div>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
data: {
isShow: true,
n: 0
},
});
</script>
</body>
列表渲染(循环)
遍历对象
1 | <body> |
遍历数组对象
1 |
|
遍历字符串
1 | <body> |
遍历指定次数
1 | <body> |
key的注意事项
虚拟DOM中key的作用:
key是虚拟DON对象的标识,当状态中的数据发生变化时,Vue会根据【新数据】生成【新的虚拟DON】,
随后Vue进行【新虚拟DOM】与【旧虚拟DOM】的差异比较,比较规则如下:对比规则:
旧虚拟DOM中找到了与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
若虚拟DOM中内容没变,直接使用之前的真实DOM
若虚拟DOM中内容变了,则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换掉页面中之前的真实DOM。旧虚拟DOM中未找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key
创建新的真实DOM,随后渲染到到页面。
- 用index作为key可能会引发的问题:
若对数据进行:逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作:
会产生没有必要的真实DOM更新==>界面效果没问题,但效率低。
- 如果结构中还包含输入类的DOM:
会产生错误DOM更新==>界面有问题。
4.开发中如何选择key? :
- 最好使用每条数据的唯一标识作为key,比如id、手机号、身份证号、学号等唯一值。
- 如果不存在对数据的逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作,仅用于渲染列表用于展示,使用index作为key是没有问题的。
列表过滤
监听实现
1 | <body> |
计算属性实现
1 | <body> |
列表排序
1 | <body> |
数据监测
Vue监视数据的原理
vue会监视data中所有层次的数据。
如何监测对象中的数据?
- 通过setter实现监视,且要在new Vue时就传入要监测的数据。
- 对象中后追加的属性,Vue默认不做响应式处理
- 如需给后添加的属性做响应式,请使用如下API:
Vue.set(target.propertyName/index,value)vm.$set(target.propertyName/index,value)
- 如何监测数组中的数据?
- 通过包裹数组更新元素的方法实现,本质就是做了两件事:
调用原生对应的方法对数组进行更新。
重新解析模板,进而更新页面。
- 在Vue修改数组中的某个元素一定要用如下方法:
- 使用这些API:
push()、pop()、shift()、unshift()、splice()、sort()、reverse() Vue.set()或vm.$set()
特别注意:
Vue.set()和vm.$set())不能给vm或vm的根数据对象添加属性!!!
示例
1 | <body> |
收集表单数据
text
若:<input type="text"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,用户输入的就是value值。
radio
若:<input type="radio"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,且要给标签配置value值。
checkbox
若: <input type="checkbox" />
1.没有配置input的value属性,那么收集的就是checked(勾选or未勾选,是布尔值)
2.配置input的value属性:
v-model的初始值是非数组,那么收集的就是checked(勾选 or未勾选,是布尔值)
v-model的初始值是数组,那么收集的的就是value组成的数组
三个修饰符
lazy:失去焦点再收集数据
number:输入字符串转为有效的数字
trim:输入首尾空格过滤
示例
1 | <body> |
过滤器
1 | <body> |
内置指令
v-text
将text解析到页面上
1 | <body> |
v-html
将html字符串解析到页面上
1 | <body> |
v-clock
本质是一个特殊属性,Vue实例创建完毕并接管容器后,会删掉v-cloak属性。
使用css配合v-cloak可国解决网连慢时页面展示出的问题。
1 |
|
v-once
只渲染一次,不更新,用于优化性能
1 | <body> |
v-pre
跳过vue解析节点,用于优化
1 | <body> |
自定义指令
局部指令
写法一
1 | <body> |
写法二(简写)
1 | <body> |
全局指令
1 | <body> |
生命 周期
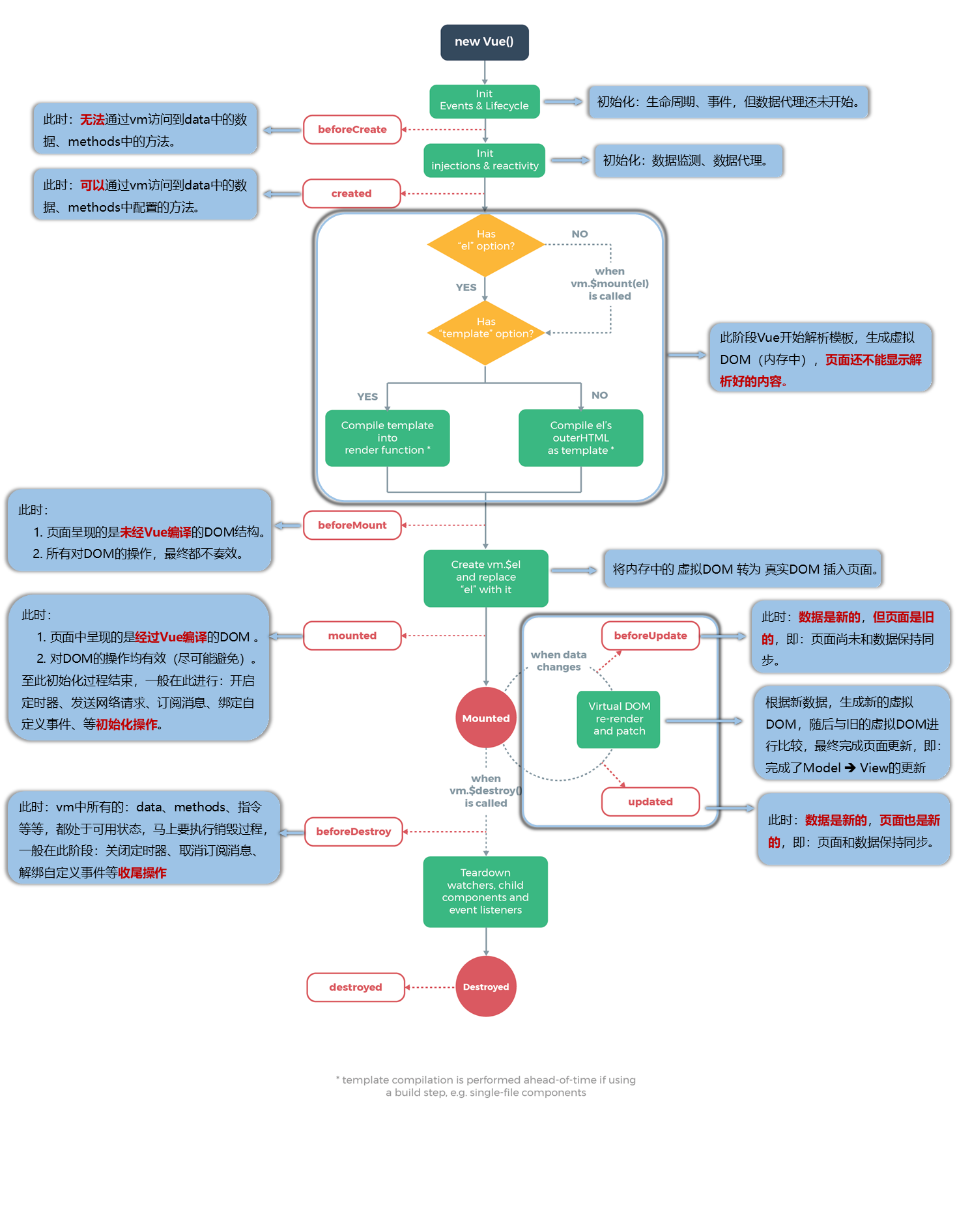
需要详细写
1 | <body> |
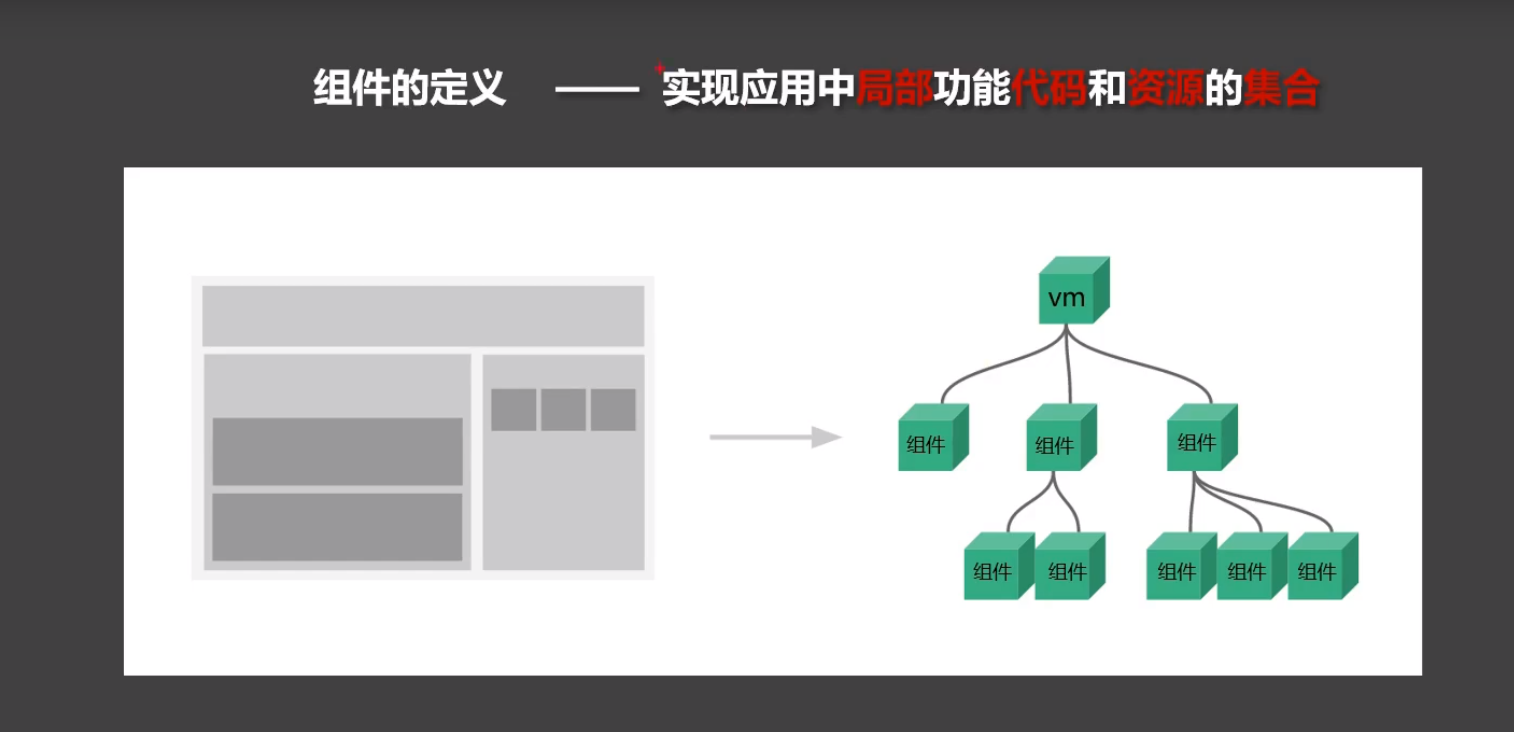
组件
理解组件
传统方式编写应用
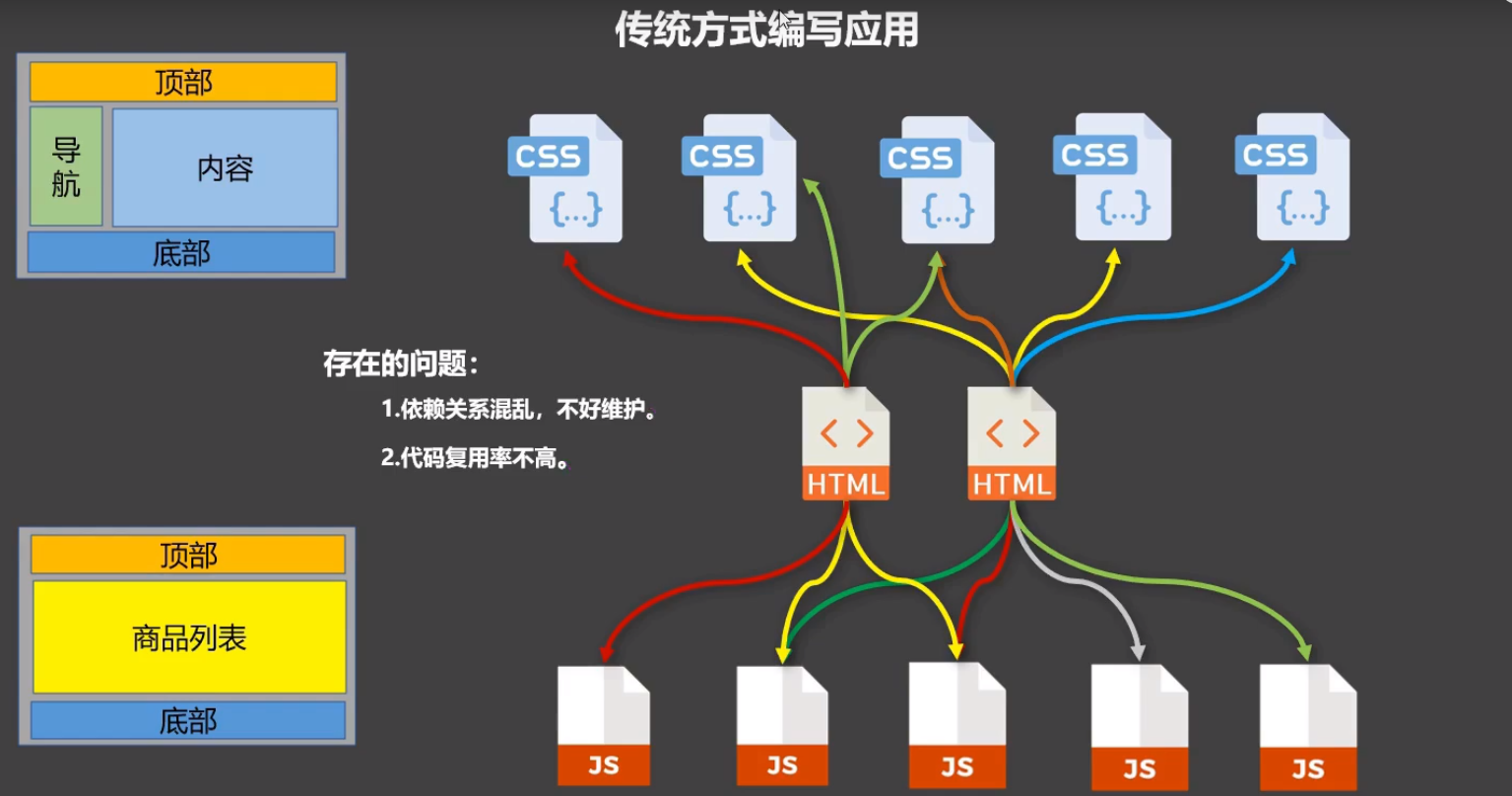
组件方式编写应用
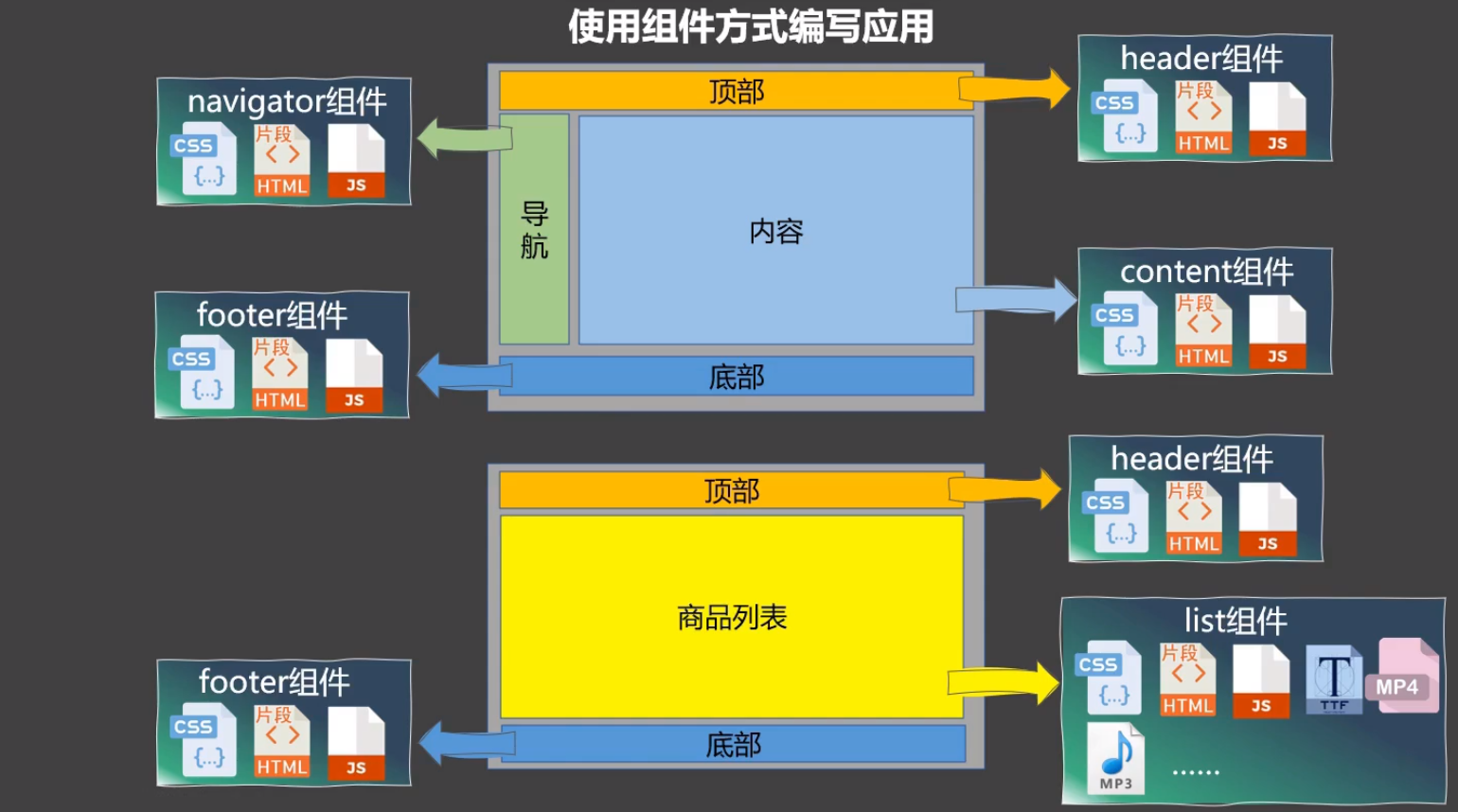
组件的定义
非单文件组件
我们若想要一个以下的界面,
根据我们前面的知识我们很容易就能写出如下代码
1 | <body> |
-
可以看出其实界面可以分为2个组件来写
若用单文件组件形式写则为
1 | <body> |
-
组件的嵌套
1 | <body> |
VueComponents
1 | <body> |
-
- 组件本质是一个名为
VueComponent的构造函数,且不是程序员定义的,是Vue.extend生成的。 - 我们只需要写
<school/>或<school></school>,Vue解析时会帮我们创建school组件的实例对象,即vue帮我们执行的:new Vuecomponent(options)。 - 特别注意:每次调用Vue.extend,返回的都是一个全新的
VueComponent! ! !! - 关于this指向:
- 组件配置中:
- data函数、methods中的函数、watch中的函数、computed中的函数它们的this均是【VueComponent实例对象】.
- new Vue(options)配置中:
- data函数、methods中的函数、watch中的函数、computed中的函数它们的this均是【Vue实例对象】。
- 组件配置中:
- VueComponent的实例对象,以后简称vc(也可称之为:组件实例对象)。
- vm(Vue实例对象)
内置关系
- 组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,
- 因为组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与 new Vue 接收相同的选项,
- 例如 data、computed、watch、methods 以及生命周期钩子等。
- 仅有的例外是像 el 这样根实例特有的选项。
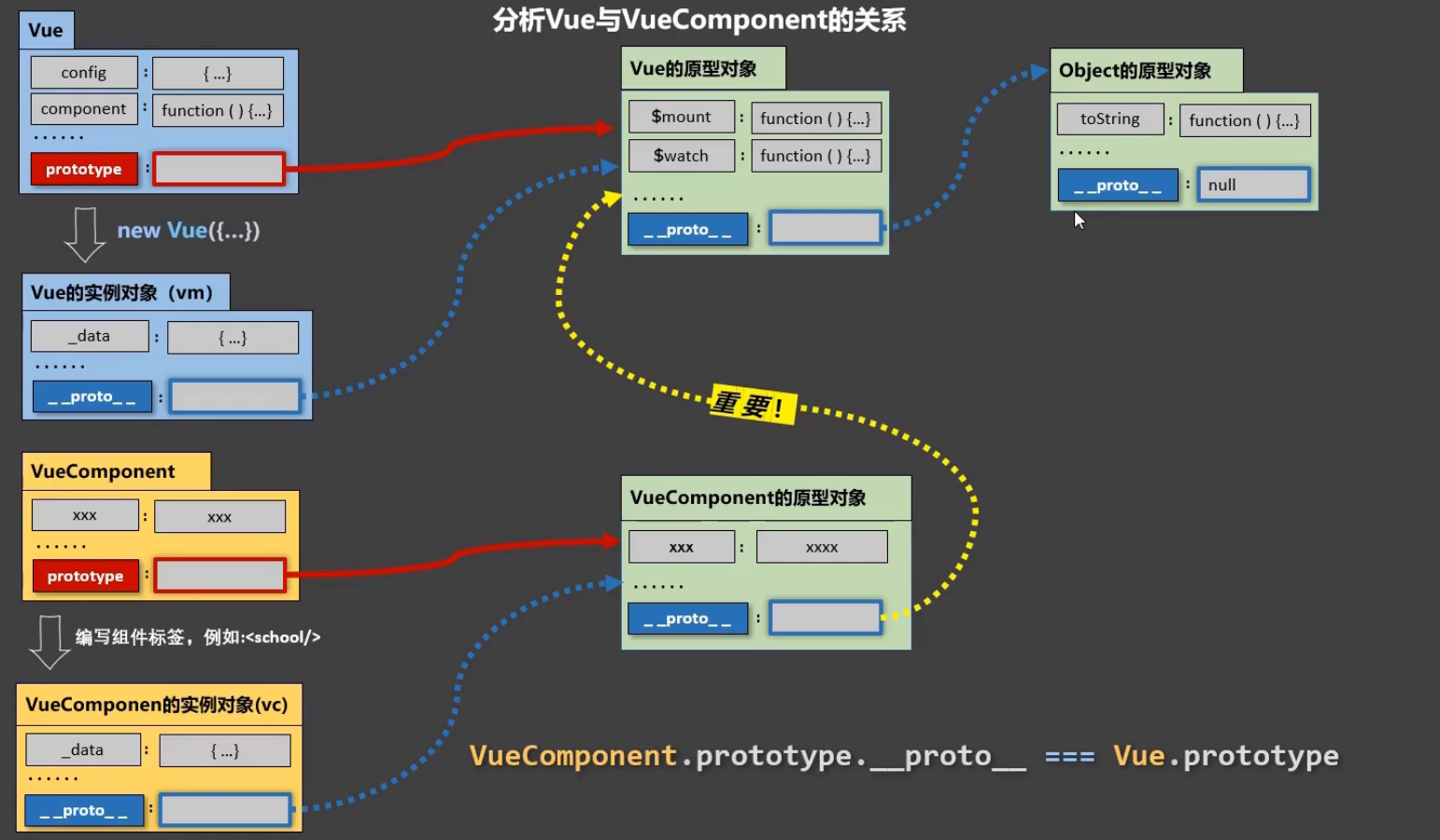
- 一个重要的内置关系:
VueComponent.prototype.__proto__ === Vue.prototype - 为什么要有这个关系: 让组件实例对象(vc)可以访问到Vue原型上的属性、方法。
1 | <body> |
-
补充
1.关于组件名
- 一个单词组成:
- 第一种写法(首字母小写):
school - 第二种写法(首字母大写):
School
- 第一种写法(首字母小写):
- 多个单词组成:
- 第一种写法(kebab-case命名):
my-school - 第二种写法(Camelcase命名):
MySchool(需要Vue脚手架支持)
- 第一种写法(kebab-case命名):
- 备注:
- 组件名尽可能回避HTML中已有的元素名称,例如: h2、H2都不行。
- 可以使用name配置项指定组件在开发者工具中呈现的名字。
2.关于组件标签;
- 第一种写法:
<schpol></school> - 第二种写法:
<school/> - 备注:不用使用脚手架时,
<school/>会导致后续组件不能渲染。
3.一个简写方式:
const school = Vue.extend(options)
可简写为:const school = options
单文件组件
组件的基本语法
1 | <template> |
举例
创建项目
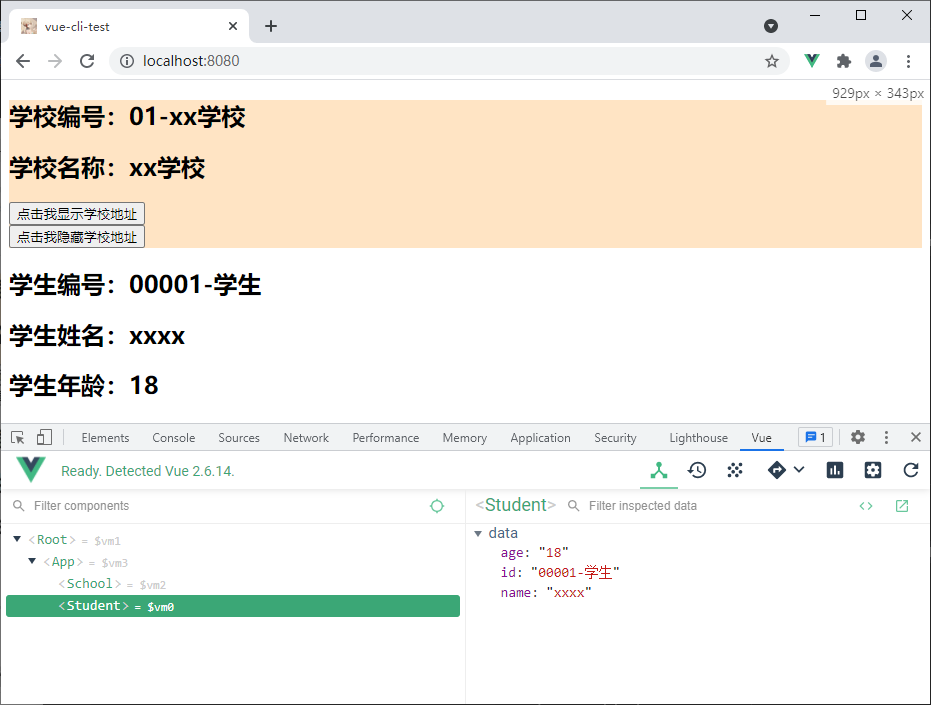
先根据上面脚手架创建方式创建脚手架,创建完成如图:
![]()
按照以下目录结构创建相应文件
![]()
\src\components\School.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37<template>
<!-- 组件的模板 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校编号:{{ id }}</h2>
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2 v-if="n === 1">学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
<button @click="n = 1">点击我显示学校地址</button>
<br />
<button @click="n = 0">点击我隐藏学校地址</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "School",
data() {
return {
n: 0,
id: "01-xx学校",
name: "xx学校",
address: "xxxxxxxxx街第xx号",
};
},
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.id);
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式*/
.demo {
background-color: bisque;
}
</style>\src\components\Student.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23<template>
<!-- 组件的模板 -->
<div>
<h2>学生编号:{{ id }}</h2>
<h2>学生姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{ age }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 组件的交互方式
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
id: "00001-学生",
name: "xxxx",
age: "18",
};
},
};
</script>\src\App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<template>
<div>
<School></School>
<Student></Student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import School from "./components/School.vue";
import Student from "./components/Student.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
School,
Student,
},
};
</script>
<style>
</style>\src\main.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14/**
* 整个项目的入口文件
*/
//引入Vue
import Vue from "vue";
//引入App组件,所有项目的父组件
import App from "./App.vue";
//关闭Vue的生产提醒
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
//将App组件放进容器中
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount("#app");public\index.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico" />
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>运行
vue-cli-service serve,访问http://localhost:8080/![]()
脚手架
webPack
webPack 很麻烦 故不考虑
Vue CLI
安装
1 | npm install -g @vue/cli |
查看版本
1 | vue --version |
升级
1 | npm update -g @vue/cli |
创建
1 | vue create name |
默认选项回车
执行时有如下输出
脚手架配置文件
查看脚手架配置
1 | vue inspect > output.js |
更改脚手架配置
请参考 https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/config/
1 | module.exports = { |
ref属性
解释
- 被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id的替代者)
- 应用在html标签上获取的是真实DOM元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
- 使用方式:
- 打标识:
<h1 ref="xxx">...</h1>或<School ref="xxx"></School> - 获取:
this.$refs.xxx
- 打标识:
举例
创建如下组件
1 | <template> |
在App组件中引用,并修改App组件如下
1 | <template> |
props
- 让组件接收外部的数据
- props是只读的,Vue底层会监测你对props的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告,
- 若业务需求确实需要修改,那么请复制props的内容到data中一份,然后去修改data中的数据。
简单接收参数
定义组件
1 | <template> |
调用组件并传入值
1 | <template> |
限制传入参数类型
修改组件
1 | <template> |
调用与上方相同
标准写法
1 | <template> |
mixin 混入/混合
将多个组件公用的配置提取成一个混入对象
举例(局部混入)
创建公用配置项文件
- mixin.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14export const mixin1 = {
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name);
},
},
};
export const mixin2 = {
data() {
return {
msg: "一条消息",
};
},
};
声明两个组件并引入公用配置
School.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mixin1, mixin2 } from "../mixin";
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
address: "xxxx街道xxx号",
};
},
mixins: [mixin1, mixin2],
};
</script>Student.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2 @click="showName">学生名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入一个混合
import { mixin1, mixin2 } from "../mixin";
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
sex: "男",
};
},
mixins: [mixin1, mixin2],
};
</script>
全局混入
mixin.js依旧不变
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14export const mixin1 = {
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name);
},
},
};
export const mixin2 = {
data() {
return {
msg: "一条消息",
};
},
};在main.js配置全局 mixin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
import { mixin1, mixin2 } from "./mixin";
// Vue.mixin({ mixin1, mixin2 });
Vue.mixin(mixin1);
Vue.mixin(mixin2);
new Vue({
//将App组件放进容器中
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount("#app");
插件
定义
1 | export default { |
引入
1 | import plugins from "./plugins"; |
使用示例
- 自定义插件plugins.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33export default {
install(Vue) {
console.log("这个是一个自定义的插件:\v", Vue);
//全局过滤器
Vue.filter("mySlice", function(text, length, suffix = "...") {
return text.slice(0, 4);
});
//自定义内置指令
Vue.directive("big", {
bind(element, binding) {
console.log("bind");
element.value = binding.value;
},
inserted(element, binding) {
element.focus();
console.log("inserted");
},
update(element, binding) {
console.log("update");
element.value = binding.value;
},
});
Vue.mixin({});
//这个方法vm与vc都能用
Vue.prototype.hello = function() {
alert("hello");
};
},
}; - 引入插件:在main.js中使用
useapi引入自定义插件使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
//引入使用
import plugins from "./plugins";
Vue.use(plugins);
new Vue({
//将App组件放进容器中
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount("#app"); - 使用插件:在
Student.vue中使用插件中的方法还有自定义指令
App.vueStudent.vue1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<template>
<div>
<Student />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from "./components/Student.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Student },
data() {
return {};
},
};
</script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<template>
<div>
<h2>学生名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<input type="text" v-big:value="name" /><br />
<button @click="hello">点我出现全局弹框</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入一个混合
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
sex: "男",
};
},
};
</script>
scoped 样式
解释
让样式在局部生效防止冲突
示例
有如下2个组件
- School.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
address: "xxxx街道xxx号",
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
.demo {
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style> - Student.vue在这两个组件中,有两个同名样式,同时使用这两个组件 会导致先导入的组件样式被覆盖,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>学生名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入一个混合
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
sex: "男",
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
.demo {
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
在<style >中加入scoped可解决1
2
3
4
5<style scoped>
.demo {
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
ToDo-list(案例)组件编码流程
需求
增删改查的 ToDo-list案例
实现静态组件
抽取(拆分)组件
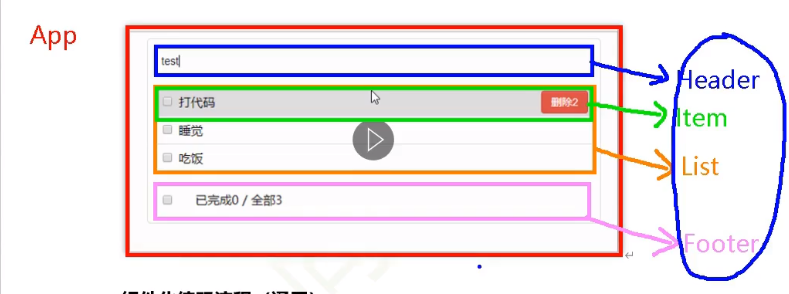
使用组件实现静态页面
仅仅实现静态界面
ToDoHeader.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车键确认" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoHeader",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.todo-header input {
width: 560px;
height: 28px;
font-size: 14px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
.todo-header input:focus {
outline: none;
border-color: rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.8);
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.075),
0 0 8px rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.6);
}
</style>ToDoList.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem />
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
data() {
return {};
},
};
</script>ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60<template>
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" />
<span>xxxxx</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" style="display:none">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
data() {
return {
name: "xxx",
address: "xxxx街道xxx号",
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
</style>ToDoFooter.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47<template>
<div class="todo-footer">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" />
</label>
<span> <span>已完成0</span> / 全部2 </span>
<button class="btn btn-danger">清除已完成任务</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoFooter",
data() {
return {
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*footer*/
.todo-footer {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
padding-left: 6px;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.todo-footer label {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.todo-footer label input {
position: relative;
top: -1px;
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 5px;
}
.todo-footer button {
float: right;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader />
<ToDoList />
<ToDoFooter />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {};
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),
0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
展示动态数据
设计数据模型
数据类型应为一个对象数组,如下所示
1 | //id: 事件的Id |
展示数据
修改ToDoList.vue 组件中
<template/> 与 <script/>内容,以渲染<ToDoItem/>组件1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem v-for="todoObj in todos" :key="todoObj.id" :todoObj="todoObj" />
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
data() {
return {
todos: [
{ id: "001", text: "吃饭", done: false },
{ id: "002", text: "睡觉", done: false },
{ id: "003", text: "打豆豆", done: true },
],
};
},
};
</script>在
<ToDoList/>组件中定义todos对象数组,并根据todos循环渲染<ToDoItem/>组件,渲染时 将值传入<ToDoItem/>组件修改ToDoList.vue 组件中
<template/> 与 <script/>内容,以展示数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<template>
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" :checked="todoObj.done" />
<span>{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" style="display:none">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: {
todoObj: {
type: Object,
},
},
};
</script>在
<ToDoItem/>组件中接收<ToDoList/>传入的参数,并展示在界面
交互
添加一个todo
问题
添加todo实质是向todos数组里面添加新对象,但是我们的 todos数组是定义在ToDoList组件中的。ToDoHeader组件目前无法访问到ToDoList组件中的数据,所以我们要将todos数组换个方式定义。
解决方案
其实问题本质就是想让平级组件互相访问同一个对象数组变量,有很多方式可以实现,比如:mixin、、、
我们这里直接用最基础的方式,将todos数组定义在公共父组件App.vue中。
实现
修改
App.vue组件中<template>和<script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader :addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList :todos="todos" />
<ToDoFooter />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: [
{ id: "001", text: "吃饭", done: false },
{ id: "002", text: "睡觉", done: false },
{ id: "003", text: "打豆豆", done: true },
],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
},
};
</script>在
App.vue组件定义todos数组,并将todos数组传给ToDoList组件,且给ToDoHeader组件提供一个修改todos数组的方法修改
ToDoHeader.vue组件中<template>和<script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<input
type="text"
placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车键确认"
v-model="text"
@keyup.enter="add"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from "nanoid";//npm i nanoid
export default {
name: "ToDoHeader",
props: ["addTodo"],
data() {
return {
text: "",
};
},
methods: {
add() {
//校验合法性
if (!this.text.trim()) return alert("输入不能为空");
//构造todo对象
const toObj = { id: nanoid(), text: this.text, done: false };
//通知app组件添加todo对象
this.addTodo(toObj);
this.text = "";
},
},
};
</script>在
ToDoHeader.vue组件中接收App.vue组件传入的修改todos数组的方法,并新增input键盘事件使用此方法修改todos数组修改
ToDoHeader.vue组件中的<script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem v-for="todoObj in todos" :key="todoObj.id" :todoObj="todoObj" />
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
props: ["todos"],
};
</script>去除
ToDoList.vue组件中关于todos的定义,接收App.vue传入的todos
勾选功能
问题
勾选之后改变相应对象中的 done 状态
解决方案
App.vue组件给ToDoList.vue 提供一个根据Id更改done的方法,再由ToDoList.vue 提供给给ToDoItem.vue调用更改
实现
- 修改App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader :addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList :todos="todos" :changeTodo="changeTodo" />
<ToDoFooter />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: [
{ id: "001", text: "吃饭", done: false },
{ id: "002", text: "睡觉", done: false },
{ id: "003", text: "打豆豆", done: true },
],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
changeTodo(id) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done;
});
},
},
};
</script> - ToDoList.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem
v-for="todoObj in todos"
:key="todoObj.id"
:todoObj="todoObj"
:changeTodo="changeTodo"
/>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
props: ["todos", "changeTodo"],
};
</script> - ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span>{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" style="display:none">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj", "changeTodo"],
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.changeTodo(id);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
</style>
v-model
还可以使用双向数据绑定直接实现,
但是不建议使用,此方法修改了props,没报错是因为没修改引用,vue没检测到
违反了vue的使用规定
bug还是特性?
1 | <template> |
实现所有功能
根据上面两个功能实现所有功能
- ToDoHeader.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<input
type="text"
placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车键确认"
@keyup.enter="add"
v-model="text"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from "nanoid";
export default {
name: "ToDoHeader",
props: ["addTodo"],
data() {
return {
text: "",
};
},
methods: {
add() {
//校验合法性
if (!this.text.trim()) return alert("输入不能为空");
//构造todo对象
const toObj = { id: nanoid(), text: this.text, done: false };
//通知app组件添加todo对象
this.addTodo(toObj);
this.text = "";
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*header*/
.todo-header input {
width: 560px;
height: 28px;
font-size: 14px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
.todo-header input:focus {
outline: none;
border-color: rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.8);
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.075),
0 0 8px rgba(82, 168, 236, 0.6);
}
</style> - ToDoList.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem
v-for="todoObj in todos"
:key="todoObj.id"
:todoObj="todoObj"
:changeTodo="changeTodo"
:deleteTodo="deleteTodo"
/>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
props: ["todos", "changeTodo", "deleteTodo"],
};
</script> - ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span>{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="hasDelete(todoObj.id)">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj", "changeTodo", "deleteTodo"],
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.changeTodo(id);
},
hasDelete(id) {
if (confirm("确定删除?")) {
this.deleteTodo(id);
}
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover {
background-color: rgb(192, 192, 192);
}
li:hover button {
display: block;
}
</style> - ToDoFooter.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73<template>
<div class="todo-footer">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isAll" />
</label>
<span>
<span>已完成 {{ hasDone }}</span> / 全部 {{ total }}
</span>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="cleanHasDone">清除已完成任务</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoFooter",
props: ["todos", "checkAllTodo", "clearTodo"],
computed: {
total() {
return this.todos.length;
},
hasDone() {
return this.todos.reduce(
(pre, current) => pre + (current.done ? 1 : 0),
0
);
},
isAll: {
get() {
return this.total === this.hasDone && this.total > 0;
},
set(value) {
this.checkAllTodo(value);
},
},
},
methods: {
cleanHasDone() {
this.clearTodo(
this.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.done == false;
})
);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.todo-footer {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
padding-left: 6px;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.todo-footer label {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.todo-footer label input {
position: relative;
top: -1px;
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 5px;
}
.todo-footer button {
float: right;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style> - App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader :addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList
:todos="todos"
:changeTodo="changeTodo"
:deleteTodo="deleteTodo"
/>
<ToDoFooter
:todos="todos"
:checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo"
:clearTodo="clearTodo"
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: [
{ id: "001", text: "吃饭", done: false },
{ id: "002", text: "睡觉", done: false },
{ id: "003", text: "打豆豆", done: true },
],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
changeTodo(id) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done;
});
},
deleteTodo(id) {
this.todos = this.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.id !== id;
});
},
checkAllTodo(done) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
todo.done = done;
});
},
clearTodo(todos) {
this.todos = todos;
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),
0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
总结
- 组件化编码流程:
- 拆分静态组件:组件要按照功能点拆分,命名不要与html元素冲突。
- 实现动态组件:考虑好数据的存放位置,数据是一个组件在用,还是一些组件在用:
- 一个组件在用:放在组件自身即可。
- 一些组件在用:放在他们共同的父组件上(状态提升)。
- 实现交互:从绑定事件开始。
- props适用于:
- 父组件==>子组件通信
- 子组件==>父组件通信(要求父先给子一个函数)
- 使用v-model时要切记: v-model绑定的值不能是props传过来的值,因为props是不可以修改的!
- props传过来的若是对象类型的值,修改对象中的属性时Vue不会报错,但不推荐这样做。
浏览器的本地存储
localStorage
大约5M左右,重启浏览器还在
1 | <body> |
SessionStorage
大约5M左右,会话失效后消失
1 |
|
应用
优化 todoList 案例
修改 App.vue <script/> 使 使用localStorage Api将数据对象存入浏览器存储中并添加监视实时更新数据。
1 | <script> |
其他写法
ps:也可以配合插件使用
删除App.vue中的data() {}配置,定义如下插件并全局混入组件
提供思路此处不详细实现
1 | export default { |
自定义事件
旧写法
先看如下一个示例:
School.Vue
1 | <template> |
App.Vue
1 | <template> |
可以轻松看出,此示例为通过父组件给子组件传递函数类型的props,实现子给父传递数据。
绑定写法1
v-on:myDiyEventName="methodName"
App.vue
1 | <!-- 第一种写法 --> |
Student.vue
1 | <template> |
简写:
@myDiyEventName=”methodName”
1 | <template> |
绑定写法2
<Student ref="refname" />
this.$refs.refname.$on("myDiyEventName", this.methodName);
App.vue
1 | <template> |
Student.vue
与写法1相同
解绑
解绑某自定义事件
this.$off('myDiyEventName');
解绑多个自定义事件
this.$off(['myDiyEventName1','myDiyEventName2']);
解绑所有
this.$off();
现在我们定义一个自定义事件
总结
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于:子组件 ===> 父组件
使用场景:A是父组件,B是子组件,B想给A传数据,那么就要在A中给B绑定自定义事件(事件的回调在A中)。
绑定自定义事件:
- 第一种方式,在父组件中:
<Demo @atguigu="test"/>或<Demo v-on:atguigu="test"/> - 第二种方式,在父组件中:
1
2
3
4<Demo ref="demo"/>
mounted(){
this.$refs.xxx.$on('atguigu',this.test)
} - 若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用
once修饰符,或$once方法。
- 第一种方式,在父组件中:
触发自定义事件:
this.$emit('atguigu',数据)解绑自定义事件
this.$off('atguigu')组件上也可以绑定原生DOM事件,需要使用
native修饰符。注意:通过
this.$refs.xxx.$on('atguigu',回调)绑定自定义事件时,回调要么配置在methods中,要么用箭头函数,否则this指向会出问题!
应用到TodoList项目上
修改 ToDoFooter.vue与 ToDoHeader.vue组件为自定义事件
ToDoHeader.vue
1 | <template> |
ToDoFooter.vue
1 | <template> |
App.vue
1 | <template> |
全局事件总线
作用
(GlobalEventBus) 一种组件之间的通信方式,用于任意组件间通信
使用
安装全局事件总线
1 | import Vue from "vue"; |
使用
接受数据
mounted() {
//将事件绑定到事件总线上
this.bus.$on("EventName", (param) => {
console.log("组件回调:", param);
});
},
beforeDestroy() {
//将事件从全局事件总线上解绑
this.bus.$off("EventName");
},
1 | <template> |
提供数据
this.bus.$emit("EventName", {param}});
1 | <template> |
实例
优化todoList App组件 与Item 组件的通信
App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader @addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList :todos="todos" />
<ToDoFooter
:todos="todos"
@checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo"
@clearTodo="clearTodo"
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("todos")) || [],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
checkAllTodo(done) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
todo.done = done;
});
},
clearTodo(todos) {
this.todos = todos;
},
changeTodo(id) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done;
});
},
deleteTodo(id) {
this.todos = this.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.id !== id;
});
},
},
watch: {
todos: {
deep: true,
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
localStorage.setItem("todos", JSON.stringify(newValue));
},
},
},
mounted() {
this.bus.$on("changeTodo", this.changeTodo);
this.bus.$on("deleteTodo", this.deleteTodo);
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.bus.$off("changeTodo", "deleteTodo");
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),
0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>ToDoList.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<ToDoItem v-for="todoObj in todos" :key="todoObj.id" :todoObj="todoObj" />
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoItem from "./ToDoItem";
export default {
name: "ToDoList",
components: { ToDoItem },
props: ["todos"],
};
</script>ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span>{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="hasDelete(todoObj.id)">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj"],
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.bus.$emit("changeTodo", id);
},
hasDelete(id) {
if (confirm("确定删除?")) {
this.bus.$emit("deleteTodo", id);
// this.deleteTodo(id);
}
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover {
background-color: rgb(192, 192, 192);
}
li:hover button {
display: block;
}
</style>
消息订阅与发布
安装相关库
npm i pubsub-js
订阅/取消订阅 消息
//订阅消息
this.pubId = pubsub.subscribe("getStudentName", (msgName, data) => {
console.log(this);
console.log("有人发布了" + msgName + "消息:", data);
});
//取消订阅
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pubId);
1 | <template> |
发布消息
//发布名为 getStudentName 的消息
pubsub.publish("getStudentName", 666);
1 | <template> |
实例
优化todoList App组件 与Item 组件的通信
优化Item中删除todo的消息传递
App.vue 订阅消息
deleteTodo1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader @addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList :todos="todos" />
<ToDoFooter
:todos="todos"
@checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo"
@clearTodo="clearTodo"
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("todos")) || [],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
checkAllTodo(done) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
todo.done = done;
});
},
clearTodo(todos) {
this.todos = todos;
},
changeTodo(id) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done;
});
},
deleteTodo(msgName, id) {
this.todos = this.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.id !== id;
});
},
},
watch: {
todos: {
deep: true,
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
localStorage.setItem("todos", JSON.stringify(newValue));
},
},
},
mounted() {
this.bus.$on("changeTodo", this.changeTodo);
this.deleteTodoMsgId = pubsub.subscribe("deleteTodo", this.deleteTodo);
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.bus.$off("changeTodo");
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.deleteTodoMsgId);
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),
0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>ToDoItem.vue 发布消息
deleteTodo1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span>{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="hasDelete(todoObj.id)">
删除
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj"],
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.bus.$emit("changeTodo", id);
},
hasDelete(id) {
if (confirm("确定删除?")) {
pubsub.publish("deleteTodo", id);
}
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover {
background-color: rgb(192, 192, 192);
}
li:hover button {
display: block;
}
</style>
$nextTick
功能
- 语法:
this.$nextTick(回调函数) - 作用:在下一次 DOM 更新结束后执行其指定的回调。
- 什么时候用:当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新DOM进行某些操作时,要在nextTick所指定的回调函数中执行。
ToDo-list(案例)新增修改功能
- App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171<template>
<div>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-wrap">
<ToDoHeader @addTodo="addTodo" />
<ToDoList :todos="todos" />
<ToDoFooter
:todos="todos"
@checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo"
@clearTodo="clearTodo"
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ToDoHeader from "./components/ToDoHeader.vue";
import ToDoList from "./components/ToDoList.vue";
import ToDoFooter from "./components/ToDoFooter.vue";
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { ToDoHeader, ToDoList, ToDoFooter },
data() {
return {
todos: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("todos")) || [],
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(todoObj) {
this.todos.unshift(todoObj);
},
checkAllTodo(done) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
todo.done = done;
});
},
clearTodo(todos) {
this.todos = todos;
},
changeTodo(id) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) todo.done = !todo.done;
});
},
deleteTodo(msgName, id) {
this.todos = this.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.id !== id;
});
},
hasEditTodo(_, todoObj) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === todoObj.id) {
if (todo.isEdit == true) {
todo.isEdit = !todo.isEdit;
} else {
this.$set(todo, "isEdit", true);
}
}
});
},
updateTodo(_, todoObj) {
this.todos.forEach((todo) => {
if (todo.id === todoObj.id) {
todo.text = todoObj.text;
}
});
},
},
watch: {
todos: {
deep: true,
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
localStorage.setItem("todos", JSON.stringify(newValue));
},
},
},
mounted() {
this.bus.$on("changeTodo", this.changeTodo);
this.deleteTodoMsgId = pubsub.subscribe("deleteTodo", this.deleteTodo);
this.hasEditTodoMsgId = pubsub.subscribe("hasEditTodo", this.hasEditTodo);
this.updateTodoMsgId = pubsub.subscribe("updateTodo", this.updateTodo);
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.bus.$off("changeTodo");
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.deleteTodoMsgId);
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.hasEditTodoMsgId);
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.updateTodoMsgId);
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*base*/
body {
background: #fff;
}
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),
0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #da4f49;
border: 1px solid #bd362f;
}
.btn-danger:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #bd362f;
}
.btn-edit {
color: #fff;
background-color: skyblue;
border: 1px solid rgb(62, 102, 117);
margin: 5px;
}
.btn-edit:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: rgb(58, 93, 107);
}
.btn:focus {
outline: none;
}
.todo-container {
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.todo-container .todo-wrap {
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
/*main*/
.todo-main {
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty {
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style> - ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span v-show="!todoObj.isEdit">{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
<input
v-show="todoObj.isEdit"
type="text"
v-model="todoObj.text"
@blur="update(todoObj, $event)"
/>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="hasDelete(todoObj.id)">
删除
</button>
<button
v-show="!todoObj.isEdit"
class="btn btn-edit"
@click="hasEdit(todoObj)"
>
编辑
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj"],
data() {
return {
text: "",
};
},
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.bus.$emit("changeTodo", id);
},
hasDelete(id) {
if (confirm("确定删除?")) {
pubsub.publish("deleteTodo", id);
}
},
hasEdit(todoObj) {
pubsub.publish("hasEditTodo", todoObj);
},
update(todoObj, e) {
//校验合法性
if (!this.todoObj.text.trim()) return alert("输入不能为空"); //通知app组件添加todo对象
pubsub.publish("updateTodo", e.target.value);
pubsub.publish("hasEditTodo", this.todoObj);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover {
background-color: rgb(192, 192, 192);
}
li:hover button {
display: block;
}
</style>
使用 $nextTick 优化
- ToDoItem.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114<template>
<li>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
:checked="todoObj.done"
@change="hasChenge(todoObj.id)"
/>
<span v-show="!todoObj.isEdit">{{ todoObj.text }}</span>
<input
v-show="todoObj.isEdit"
type="text"
v-model="todoObj.text"
@blur="update(todoObj, $event)"
ref="todoInputText"
/>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="hasDelete(todoObj.id)">
删除
</button>
<button
v-show="!todoObj.isEdit"
class="btn btn-edit"
@click="hasEdit(todoObj)"
>
编辑
</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "ToDoItem",
props: ["todoObj"],
data() {
return {
text: "",
};
},
methods: {
hasChenge(id) {
//将对应id的对象的done取反
this.bus.$emit("changeTodo", id);
},
hasDelete(id) {
if (confirm("确定删除?")) {
pubsub.publish("deleteTodo", id);
}
},
hasEdit(todoObj) {
pubsub.publish("hasEditTodo", todoObj);
this.$nextTick(function() {
this.$refs.todoInputText.focus();
});
setInterval(() => {
this.$refs.todoInputText.focus();
}, 200);
},
update(todoObj, e) {
//校验合法性
if (!this.todoObj.text.trim()) return alert("输入不能为空"); //通知app组件添加todo对象
pubsub.publish("updateTodo", e.target.value);
pubsub.publish("hasEditTodo", this.todoObj);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/*item*/
li {
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label {
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input {
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button {
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before {
content: initial;
}
li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover {
background-color: rgb(192, 192, 192);
}
li:hover button {
display: block;
}
</style>
动画效果
用法
- 作用:在插入、更新或移除 DOM元素时,在合适的时候给元素添加样式类名。
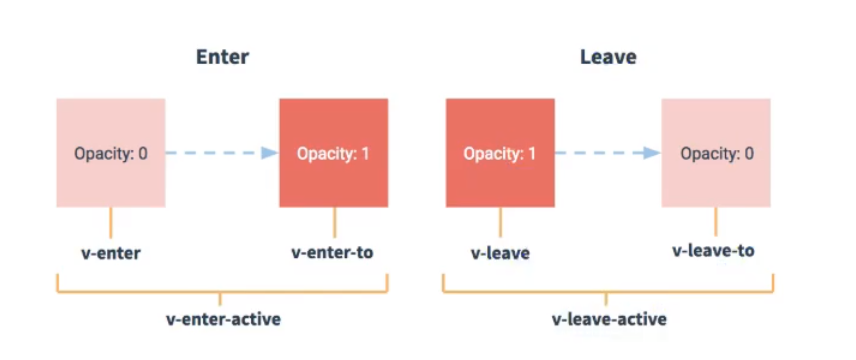
- 图示:
![]()
- 写法:
- 准备好样式:
- 元素进入的样式:
- v-enter:进入的起点
- v-enter-active:进入过程中
- v-enter-to:进入的终点
- 元素离开的样式:
- v-leave:离开的起点
- v-leave-active:离开过程中
- v-leave-to:离开的终点
- 元素进入的样式:
- 使用
<transition>包裹要过度的元素,并配置name属性:1
2
3<transition name="hello">
<h1 v-show="isShow">你好啊!</h1>
</transition> - 备注:若有多个元素需要过度,则需要使用:
<transition-group>,且每个元素都要指定key值。
- 准备好样式:
示例
动画
1 | <template> |
过渡
1 | <template> |
多个元素过渡
1 | <template> |
集成第三方动画
- 安裝
1
npm install animate.css --save
- 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<h1>isShow:{{ isShow }}</h1>
<transition
name="animate__animated animate__bounce"
enter-active-class="animate__bounceInLeft"
leave-active-class="animate__fadeOutDownBig"
appear
>
<h1 v-show="isShow">你好1</h1>
</transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import "animate.css";
export default {
name: "Test3",
data() {
return {
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
实例
优化todoList中的item组件动画
1 | <template> |
或者写在List组件中
1 | <template> |
Vue中的Ajax
解决跨域
配置代理服务器
方式1
vue.config.js
1 | module.exports = { |
- 优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端(8080)即可。
- 缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
- 工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器 (优先匹配前端资源)
方式2
vue.config.js
1 | // vue.config.js |
- 优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
- 缺点:配置略微繁琐,请求资源时必须加前缀。
实例
1.写两个服务器
package.json
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12{
"name": "server",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.17.1"
}
}server1.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.use((request,response,next)=>{
console.log('有人请求服务器1了');
console.log('请求来自于',request.get('Host'));
console.log('请求的地址',request.url);
next()
})
app.get('/students',(request,response)=>{
const students = [
{id:'001',name:'tom',age:18},
{id:'002',name:'jerry',age:19},
{id:'003',name:'tony',age:120},
]
response.send(students)
})
app.listen(5000,(err)=>{
if(!err) console.log('服务器1启动成功了,请求学生信息地址为:http://localhost:5000/students');
})server12js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.use((request,response,next)=>{
console.log('有人请求服务器2了');
next()
})
app.get('/cars',(request,response)=>{
const cars = [
{id:'001',name:'奔驰',price:199},
{id:'002',name:'马自达',price:109},
{id:'003',name:'捷达',price:120},
]
response.send(cars)
})
app.listen(5001,(err)=>{
if(!err) console.log('服务器2启动成功了,请求汽车信息地址为:http://localhost:5001/cars');
})启动
1
2node server1
node server2
2.配置代理
1 | // vue.config.js |
3.测试代理
- 安装 axios
1
npm i axios
- 发送请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40<template>
<div class="root">
<button @click="getMsg1">获取信息1</button>
<button @click="getMsg2">获取信息2</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
getMsg1() {
console.log("get=>http://localhost:8080/students");
let url5000 = "http://localhost:8080/api1/students";
axios
.get(url5000)
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
},
getMsg2() {
console.log("get=>http://localhost:8080/cars");
let url5001 = "http://localhost:8080/api2/cars";
axios
.get(url5001)
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped></style>
github用户搜索案例
App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<template>
<div class="container">
<Search />
<List />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Search from "./components/Search.vue";
import List from "./components/List.vue";
import bootstrap from "./assets/css/bootstrap.css";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Search, List },
};
</script>
<style scoped></style>Search.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57<template>
<section class="jumbotron">
<h3 class="jumbotron-heading">搜索 Github 用户</h3>
<div>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="输入用户名称"
v-model="inputName"
@keyup.enter="Search"
/>
<button @click="Search">搜索</button>
</div>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "Search",
data() {
return {
inputName: "",
};
},
methods: {
Search() {
let girhubApi = `https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${this.inputName}`;
this.$bus.$emit("uppdateUserList", {
isFirst: false,
isLoging: true,
errMsg: "",
userList: [],
});
axios
.get(girhubApi)
.then((res) => {
this.$bus.$emit("uppdateUserList", {
isFirst: false,
isLoging: false,
errMsg: "",
userList: res.data.items,
});
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
this.$bus.$emit("uppdateUserList", {
isFirst: false,
isLoging: false,
errMsg: err.message,
userList: [],
});
});
},
},
};
</script>List.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68<template>
<div class="row">
<div
v-show="info.userList.length"
class="card"
v-for="user in info.userList"
:key="user.login"
>
<a :href="user.html_url" target="_blank">
<img :src="user.avatar_url" style="width: 100px" />
</a>
<p class="card-text">{{ user.login }}</p>
</div>
<h1 v-show="info.isFirst">欢迎使用</h1>
<h1 v-show="info.isLoging">加载中......</h1>
<h1 v-show="info.errMsg">请求出错:{{ info.errMsg }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "List",
data() {
return {
info: {
userList: [],
isFirst: true,
isLoging: false,
errMsg: "",
},
};
},
methods: {
uppdateUserList(data) {
this.info = data;
},
},
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on("uppdateUserList", this.uppdateUserList);
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.album {
min-height: 50rem; /* Can be removed; just added for demo purposes */
padding-top: 3rem;
padding-bottom: 3rem;
background-color: #f7f7f7;
}
.card {
float: left;
width: 33.333%;
padding: 0.75rem;
margin-bottom: 2rem;
border: 1px solid #efefef;
text-align: center;
}
.card > img {
margin-bottom: 0.75rem;
border-radius: 100px;
}
.card-text {
font-size: 85%;
}
</style>
vue-resource
安装
npm i vue-resource
使用插件
1 | /** |
替换掉axios
1 | <template> |
slot插槽
让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入html结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于 父组件 ===> 子组件 。
默认插槽
写法
父组件中
1 | <Category> |
子组件中
1 | <template> |
示例
- Cotegory.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<slot>
<ul>
<li v-for="(data, index) in listData" :key="index">
{{ data }}---默认结构
</li>
</ul>
</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Cotegory",
props: ["listData", "title"],
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
background-color: rgb(225, 255, 255);
}
</style> - App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36<template>
<div class="container">
<Cotegory title="data1">
<img src="https://cn.vuejs.org/images/logo.svg" alt="" />
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data2">
<ul>
<li v-for="(str, index) in mydata2" :key="index">
{{ str }}--自定义结构
</li>
</ul>
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data3" :listData="mydata3" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Cotegory from "./components/Cotegory.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Cotegory },
data() {
return {
mydata1: ["1", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"],
mydata2: ["a1", "b2", "c3", "d4", "e5", "f6"],
mydata3: ["aaaa", "bbbb", "ccccc", "ddddd", "eeeeee", "fffff"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
具名插槽
写法
父组件中:
1 | <Category> |
子组件中:
1 | <template> |
示例
- Cotegory.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<slot name="slot1"> </slot>
<slot name="slot2"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Cotegory",
props: ["title"],
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
background-color: rgb(225, 255, 255);
}
</style> - App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55<template>
<div class="container">
<Cotegory title="data1">
<img slot="slot1" src="https://cn.vuejs.org/images/logo.svg" alt="" />
<a slot="slot2" href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度</a>
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data2">
<ul slot="slot1">
<li v-for="(str, index) in mydata1" :key="index">
{{ str }}--自定义结构
</li>
</ul>
<div slot="slot2">
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度1 </a>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度2 </a>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度3 </a>
</div>
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data3">
<ul slot="slot1">
<li v-for="(str, index) in mydata2" :key="index">
{{ str }}--自定义结构
</li>
</ul>
<template v-slot:slot2>
<div>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度1 </a>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度2 </a>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度3 </a>
</div>
<h1 style="text-align: center">你好</h1>
</template>
</Cotegory>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Cotegory from "./components/Cotegory.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Cotegory },
data() {
return {
mydata1: ["a1", "b2", "c3", "d4", "e5", "f6"],
mydata2: ["aaaa", "bbbb", "ccccc", "ddddd", "eeeeee", "fffff"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
作用域插槽
理解
数据在组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。
示例
- Cotegory.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<slot :listData="mydata"> </slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Cotegory",
props: ["title"],
data() {
return {
mydata: ["aaaa", "bbbb", "ccccc", "ddddd", "eeeeee", "fffff"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
background-color: rgb(225, 255, 255);
}
</style> - App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43<template>
<div class="container">
<Cotegory title="data1">
<template scope="data">
<ul>
<li v-for="(str, index) in data.listData" :key="index">
{{ str }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data1">
<template scope="{listData}">
<ol>
<li v-for="(str, index) in listData" :key="index">
{{ str }}
</li>
</ol>
</template>
</Cotegory>
<Cotegory title="data2">
<template slot-scope="{ listData }">
<h4 v-for="(str, index) in listData" :key="index">
{{ str }}
</h4>
</template>
</Cotegory>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Cotegory from "./components/Cotegory.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Cotegory },
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
Vuex
vuex 是什么?
- 专门在 Vue 中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个 Vue 插件,
- 对 vue 应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),
- 也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
- 官方文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
为什么用
- 多个组件依赖于同一状态
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态
对比全局事件总线
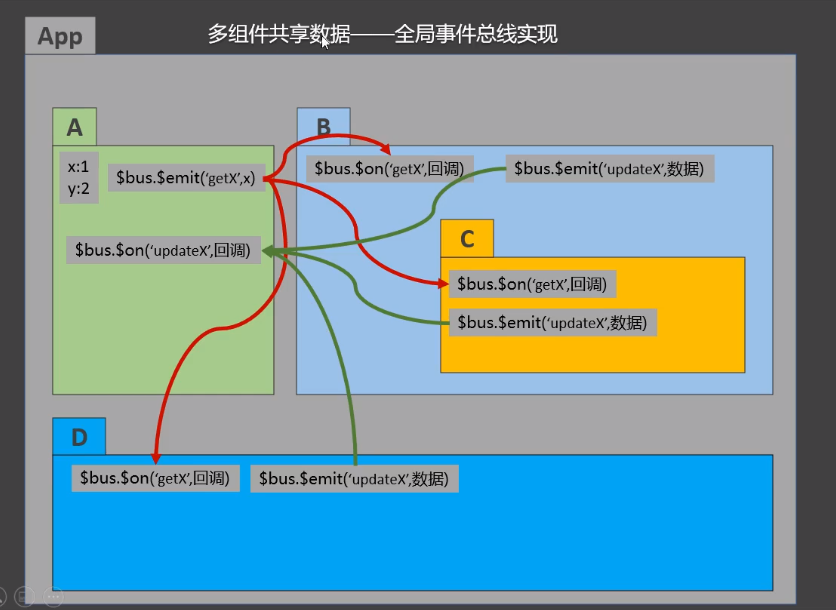
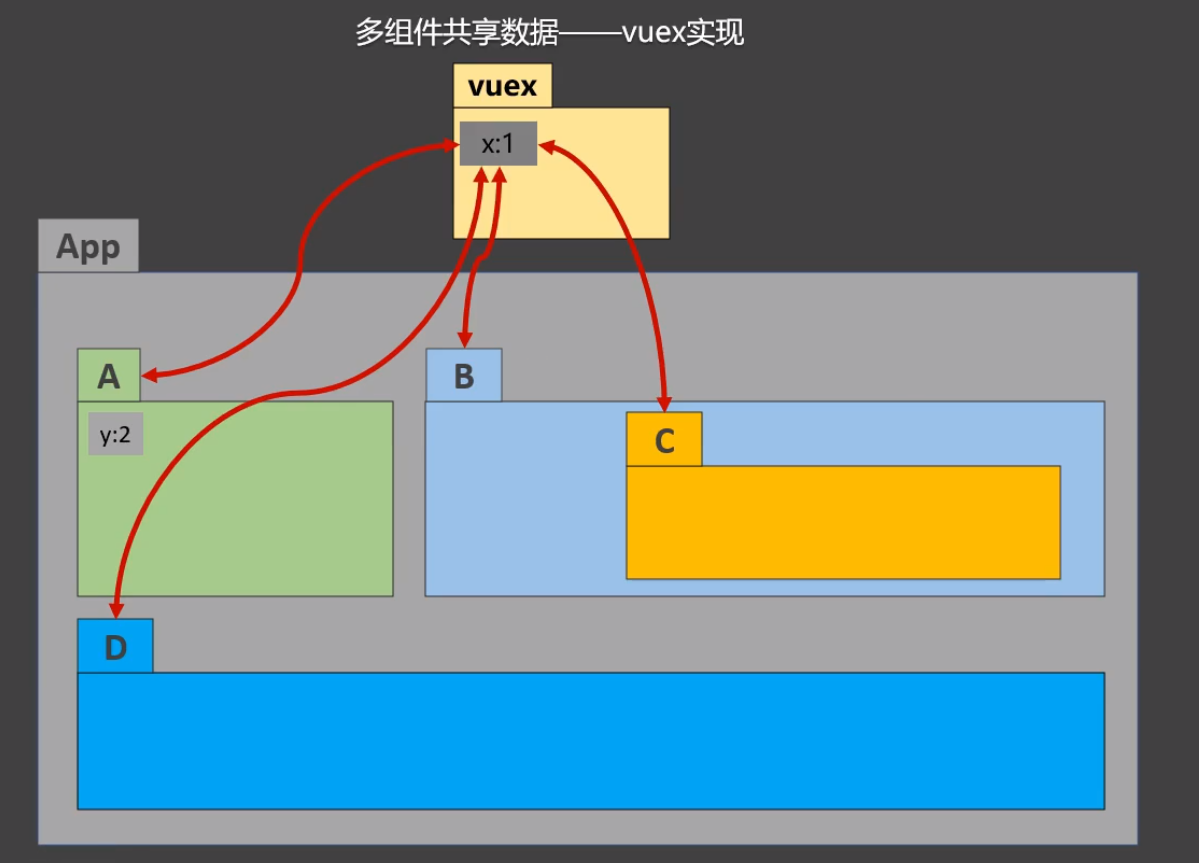
原理图
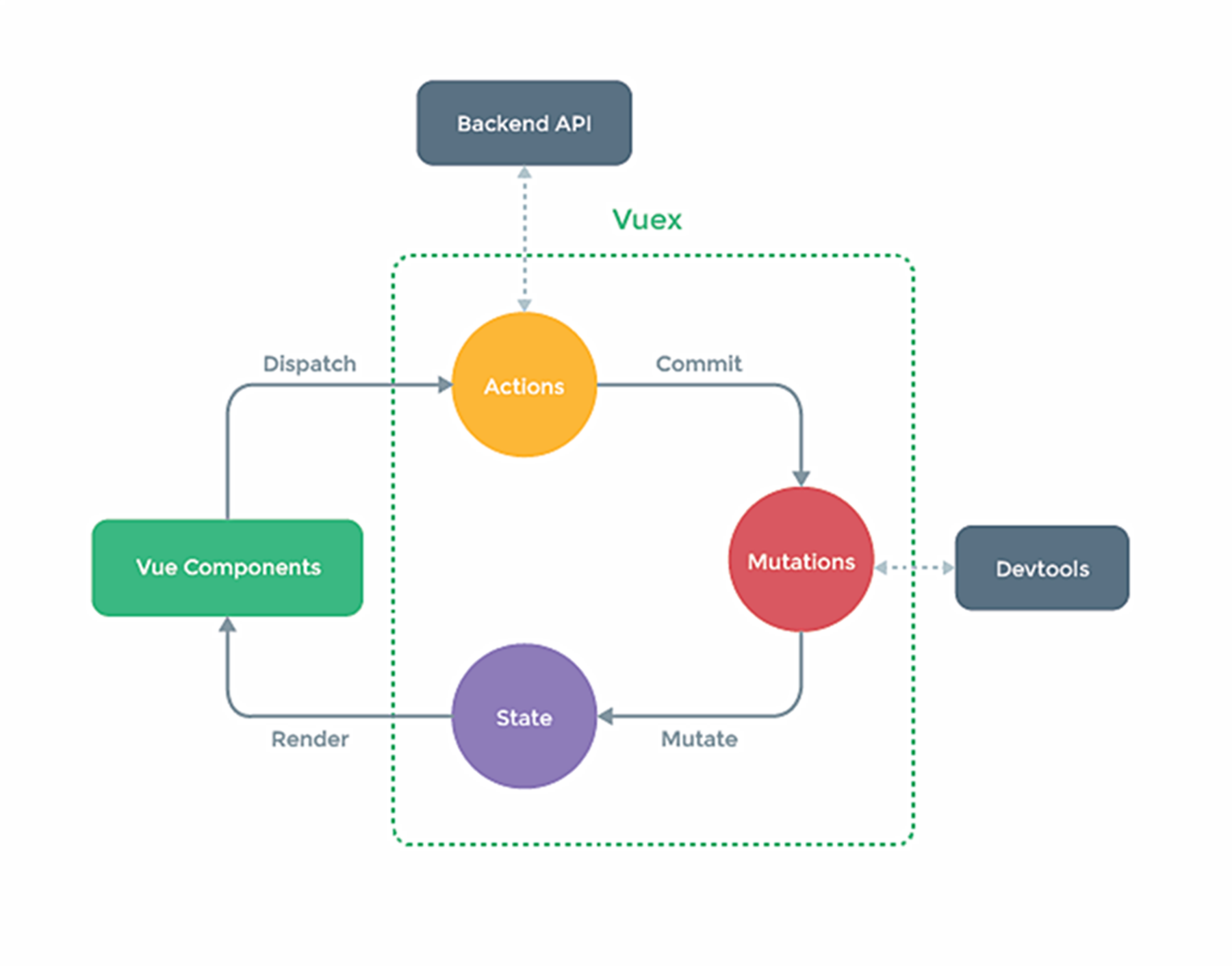
使用
安装
npm i vuex
写如下一个案例 用于测试
Count.vue
1 | <template> |
App.vue
1 | <template> |
引用插件
新建文件 /src/store/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23//用于创建最为核心的 store 文件
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
//应用vuex
Vue.use(vuex);
//准备 actions 用于相应组件中的动作
const actions = {};
//准备 mutations 用于操作数据
const mutations = {};
//准备 state 用于相应存储数据
const state = {};
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});
//导出(爆露)store
export default store;并在main.js 引入此文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20/**
* 整个项目的入口文件
*/
//引入Vue
import Vue from "vue";
//引入App组件,所有项目的父组件
import App from "./App.vue";
//关闭Vue的生产提醒
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
import store from "./store/index";
new Vue({
//将App组件放进容器中
render: (h) => h(App),
store,
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this;
},
}).$mount("#app");
使用vuex优化
将业务逻辑提炼到 vuex 中
1 | //用于创建最为核心的 store 文件 |
在组件对应的位置调用
1 | <template> |
getters配置
/src/store/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61//用于创建最为核心的 store 文件
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
//应用vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//准备 actions 用于相应组件中的动作
const actions = {
add: function(context, value) {
console.log("actions_add:", context, value);
context.commit("ADD", value);
},
sub: function(context, value) {
console.log("actions_sub:", context, value);
context.commit("SUB", value);
},
addOdd: function(context, value) {
console.log("actions_addOdd:", context, value);
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit("ADD", value);
}
},
addWait: function(context, value) {
console.log("actions_addWait:", context, value);
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit("ADD", value);
}, 1000);
},
};
//准备 mutations 用于操作数据
const mutations = {
ADD: function(state, value) {
console.log("mutations_ADD:", state, value);
state.sum += value;
},
SUB: function(state, value) {
console.log("mutations_SUB:", state, value);
state.sum -= value;
},
};
//准备 state 用于相应存储数据
const state = { sum: 0 };
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10;
},
};
//创建 store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters,
});
//导出(爆露)store
export default store;Count.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>{{ $store.state.sum }}</h1>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.bigSum }}</h2>
<select v-model.number="selectNember">
<option value="1" selected> 1</option>
<option value="2"> 2</option>
<option value="3"> 3</option>
<option value="4"> 4</option>
</select>
<button @click="addition">+</button>
<button @click="subtraction">-</button>
<button @click="additionOdd">当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button @click="additionWait">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
selectNember: 1,
};
},
methods: {
addition() {
this.$store.dispatch("add", this.selectNember);
},
subtraction() {
this.$store.dispatch("sub", this.selectNember);
},
additionOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch("addOdd", this.selectNember);
},
additionWait() {
this.$store.dispatch("addWait", this.selectNember);
},
},
mounted() {},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
button {
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
mapState & mapGetters
用途
mapState :映射 state 中的数据为计算属性
mapGetters:映射 getters 中的数据为计算属性
示例
src\store\index.js
1 | //用于创建最为核心的 store 文件 |
src\components\Count.vue
1 | <template> |
mapActions & mapMutations
用途
mapActions :用于帮助我们生成action对话方法,即$store.dispatch(xxx)
mapMutations:用于帮助我们生成mutations对话方法,即$store.commit(xxx)
示例
src\components\Count.vue
1 | <template> |
src\store\index.js
1 | //用于创建最为核心的 store 文件 |
模块化
让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
模块分类1
1 | const countAbout = { |
组件读取state
1 | //方式一:自己直接读取 |
组件读取getters
1 | //方式一:自己直接读取 |
组件调用dispatch
1 | //方式一:自己直接dispatch |
组件调用commit
1 | //方式一:自己直接commit |
路由
什么是是路由
一个路由(route)就是一组映射关系(key - value),多个路由需要路由器(router)进行管理。
为啥用?
为了实现SPA(single page web application)(单页面)应用
使用
安装
npm i vue-router
应用
Vue.use(VueRouter)
写两个简单组件
Home.vue
1 | <template> |
About.vue
1 | <template> |
编写配置项
src\router\index.js
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
引入项目
1 | import Vue from "vue"; |
编写跳转界面
1 | <template> |
注意点
- 路由组件通常存放在
pages文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。 - 通过切换,“隐藏”了的路由组件,默认是被销毁掉的,需要的时候再去挂载。
- 每个组件都有自己的
$route属性,里面存储着自己的路由信息。 - 整个应用只有一个router,可以通过组件的
$router属性获取到。
嵌套(多级)路由
src\pages\Message.vue
1 | <template> |
src\pages\News.vue
1 | <template> |
src\router\index.js
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
src\pages\Home.vue
1 | <template> |
路由传参
query参数
src\pages\Detail.vue
1 | <template> |
src\router\index.js
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
src\pages\Message.vue
1 | <template> |
params参数
src\router\index.js
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
src\pages\Detail.vue
1 | <template> |
src\pages\Message.vue
1 | <template> |
路由命名
用于简化多级路由的路径
src\router\index.js
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
1 | <router-link :to="{name:'guanyu'}">跳转到About</router-link> |
路由的props配置
让路由组件更方便的收到参数
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
replace属性
<router-link>的replace属性
作用?
控制路由跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式
理解
- 浏览器的历史记录有两种写入方式:分别为
push和replace,push是追加历史记录,replace是替换当前记录。- 路由跳转时候默认为
push
如何开启 ?
开启`replace``模式
1 | <router-link replace .......>News</router-link> |
编程式路由导航
作用?
不借助<router-link> 实现路由跳转,让路由跳转更加灵活
跳转到指定页面
1 | <template> |
前进或 后退操作
1 | this.$router.forward() //前进 |
缓存路由组件
作用
让不展示的路由组件保持挂载,不被销毁。
格式
1 | <keep-alive include="组件名"> |
路由组件生命周期
作用
路由组件所独有的两个钩子,用于捕获路由组件的激活状态。
具体名字
activated路由组件被激活时触发。deactivated路由组件失活时触发。
路由守卫
作用
对路由进行权限控制
全局守卫
全局前置路由守卫
1 | //全局前置路由守卫 |
全局后置路由守卫
1 | //全局后置路由守卫 |
独享守卫
1 | import VueRouter from "vue-router"; |
组件内守卫
1 | <template> |
两种工作模式
- 对于一个url来说,什么是hash值?—— #及其后面的内容就是hash值。
- hash值不会包含在 HTTP 请求中,即:hash值不会带给服务器。
hash模式
- 地址中永远带着#号,不美观 。
- 若以后将地址通过第三方手机app分享,若app校验严格,则地址会被标记为不合法。
- 兼容性较好。
history模式
- 地址干净,美观 。
- 兼容性和hash模式相比略差。
- 应用部署上线时需要后端人员支持,解决刷新页面服务端404的问题。
Vue UI 组件库
移动端常用 UI 组件库
- Vant https://youzan.github.io/vant
- Cube UI https://didi.github.io/cube-ui
- Mint UI http://mint-ui.github.io
PC 端常用 UI 组件库
- Element UI https://element.eleme.cn
- IView UI https://www.iviewui.com
Vue 3
Vue3 介绍
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
Vue3 带来了什么
性能提升
- 打包大小减少41%
- 初次渲染快55%, 更新渲染快133%
- 内存减少54%
- ……
源码的升级
- 使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式
- 重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking
- ……
拥抱TypeScript
- Vue3可以更好的支持TypeScript
新的特性
Composition API(组合API)
- setup配置
- ref与reactive
- watch与watchEffect
- provide与inject
- ……
新的内置组件
- Fragment
- Teleport
- Suspense
其他改变
- 新的生命周期钩子
- data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
- 移除keyCode支持作为 v-on 的修饰符
- ……
创建Vue3.0工程
使用 vue-cli 创建
创建
1 | ## 查看@vue/cli版本,确保@vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上 |
使用 vite 创建
什么是vite?
新一代前端构建工具。
优势?
- 开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动。
- 轻量快速的热重载(HMR)。
- 真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成。
- 传统构建 与 vite构建对比图
![]()
![]()
创建
1 | ## 创建工程 |
Composition API
setup
理解
- Vue3.0 中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数。
- setup 是所有Composition API(组合 API)“ 表演的舞台 ”。
- 组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在 setup 中。
- setup 函数的两种返回值:
- 若返回一个对象,则对象中的属性、方法, 在模板中均可以直接使用。(重点关注!)
- 若返回一个渲染函数:则可以自定义渲染内容。(了解)
注意点
- 尽量不要与 Vue2.x 配置混用
- Vue2.x 配置(data、methos、computed…)中可以访问到setup 中的属性、方法。
- 但在 setup 中不能访问到Vue2.x 配置(data、methos、computed…)。
- 如果有重名, setup 优先。
- setup 不能是一个 async 函数,
- 因为返回值不再是 return 的对象, 而是 promise, 模板看不到 return 对象中的属性。
- (后期也可以返回一个 Promise 实例,但需要 Suspense 和异步组件的配合)
ref 函数
作用
定义一个响应式的数据
语法
const xxx = ref(initValue)
- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference 对象,简称 ref 对象)。
- JS 中操作数据:
xxx.value - 模板中读取数据: 不需要.value,直接:
<div>{{xxx}}</div>
备注
- 接收的数据可以是:基本类型、也可以是对象类型。
- 基本类型的数据:响应式依然是靠
Object.defineProperty()的get与set完成的。 - 对象类型的数据:内部 “ 求助 ” 了 Vue3.0 中的一个新函数——
reactive函数。
reactive函数
作用
定义一个对象类型的响应式数据(基本类型不要用它,要用ref函数)
语法
const 代理对象= reactive(源对象)接收一个对象(或数组),返回一个代理对象(Proxy 的实例对象,简称 proxy 对象)
- reactive 定义的响应式数据是“深层次的”。
- 内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据进行操作。
响应式原理
vue2
实现原理
- 对象类型:通过
Object.defineProperty()对属性的读取、修改进行拦截(数据劫持)。 - 数组类型:通过重写更新数组的一系列方法来实现拦截。(对数组的变更方法进行了包裹)。
1
2
3
4Object.defineProperty(data, "count", {
get() {},
set() {},
});
存在问题
- 新增属性、删除属性, 界面不会更新。
- 直接通过下标修改数组, 界面不会自动更新。
vue3
实现原理:
- 通过 Proxy(代理): 拦截对象中任意属性的变化, 包括:属性值的读写、属性的添加、属性的删除等。
- 通过 Reflect(反射): 对源对象的属性进行操作。
- MDN 文档中描述的 Proxy 与 Reflect:
示例
1 | new Proxy(data, { |
reactive 对比 ref
- 从定义数据角度对比:
- ref 用来定义:基本类型数据。
- reactive 用来定义:对象(或数组)类型数据。
- 备注:ref 也可以用来定义对象(或数组)类型数据, 它内部会自动通过
reactive转为代理对象。
- 从原理角度对比:
- ref 通过
Object.defineProperty()的get与set来实现响应式(数据劫持)。 - reactive 通过使用Proxy来实现响应式(数据劫持), 并通过Reflect操作源对象内部的数据。
- ref 通过
- 从使用角度对比:
- ref 定义的数据:操作数据需要
.value,读取数据时模板中直接读取不需要.value。 - reactive 定义的数据:操作数据与读取数据:均不需要
.value。
- ref 定义的数据:操作数据需要
setup 的两个注意点
- setup 执行的时机
- 在 beforeCreate 之前执行一次,this 是 undefined。
- setup 的参数
- props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性。
- context:上下文对象
- attrs: 值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在 props 配置中声明的属性, 相当于
this.$attrs。 - slots: 收到的插槽内容, 相当于
this.$slots。 - emit: 分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于
this.$emit。
- attrs: 值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在 props 配置中声明的属性, 相当于
计算属性与监视
computed 函数
- 与 Vue2.x 中 computed 配置功能一致
- 写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20import {computed} from 'vue'
setup(){
...
//计算属性——简写
let fullName = computed(()=>{
return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName
})
//计算属性——完整
let fullName = computed({
get(){
return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName
},
set(value){
const nameArr = value.split('-')
person.firstName = nameArr[0]
person.lastName = nameArr[1]
}
})
}
watch 函数
- 与 Vue2.x 中 watch 配置功能一致
- 两个小“坑”:
- 监视 reactive 定义的响应式数据时:oldValue 无法正确获取、强制开启了深度监视(deep 配置失效)。
- 监视 reactive 定义的响应式数据中某个属性时:deep 配置有效。
- 情况一:监视ref定义的响应式数据
1
2
3
4
5watch(sum,(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("sum变化了", newValue, oldValue);
},
{ immediate: true }
); - 情况二:监视多个ref定义的响应式数据
1
2
3watch([sum, msg], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("sum或msg变化了", newValue, oldValue);
}); - 情况三:监视reactive定义的响应式数据
若watch监视的是reactive定义的响应式数据,则无法正确获得oldValue!!
若watch监视的是reactive定义的响应式数据,则强制开启了深度监视1
2
3
4
5watch(person,(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("person变化了", newValue, oldValue);
},
{ immediate: true, deep: false }
); //此处的deep配置不再奏效 - 情况四:监视reactive定义的响应式数据中的某个属性
1
2
3
4
5watch(() => person.job,(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("person的job变化了", newValue, oldValue);
},
{ immediate: true, deep: true }
); - 情况五:监视reactive定义的响应式数据中的某些属性
1
2
3
4
5watch([() => person.job, () => person.name],(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("person的job变化了", newValue, oldValue);
},
{ immediate: true, deep: true }
); - 特殊情况
1
2
3
4
5watch(() => person.job,(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("person的job变化了", newValue, oldValue);
},
{ deep: true }
); //此处由于监视的是reactive素定义的对象中的某个属性,所以deep配置有效
watchEffect 函数
- watch 的套路是:既要指明监视的属性,也要指明监视的回调。
- watchEffect 的套路是:不用指明监视哪个属性,监视的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监视哪个属性。
- watchEffect 有点像 computed:
- 但 computed 注重的计算出来的值(回调函数的返回值),所以必须要写返回值。
- 而 watchEffect 更注重的是过程(回调函数的函数体),所以不用写返回值。
1 | //watchEffect所指定的回调中用到的数据只要发生变化,则直接重新执行回调。 |
生命周期
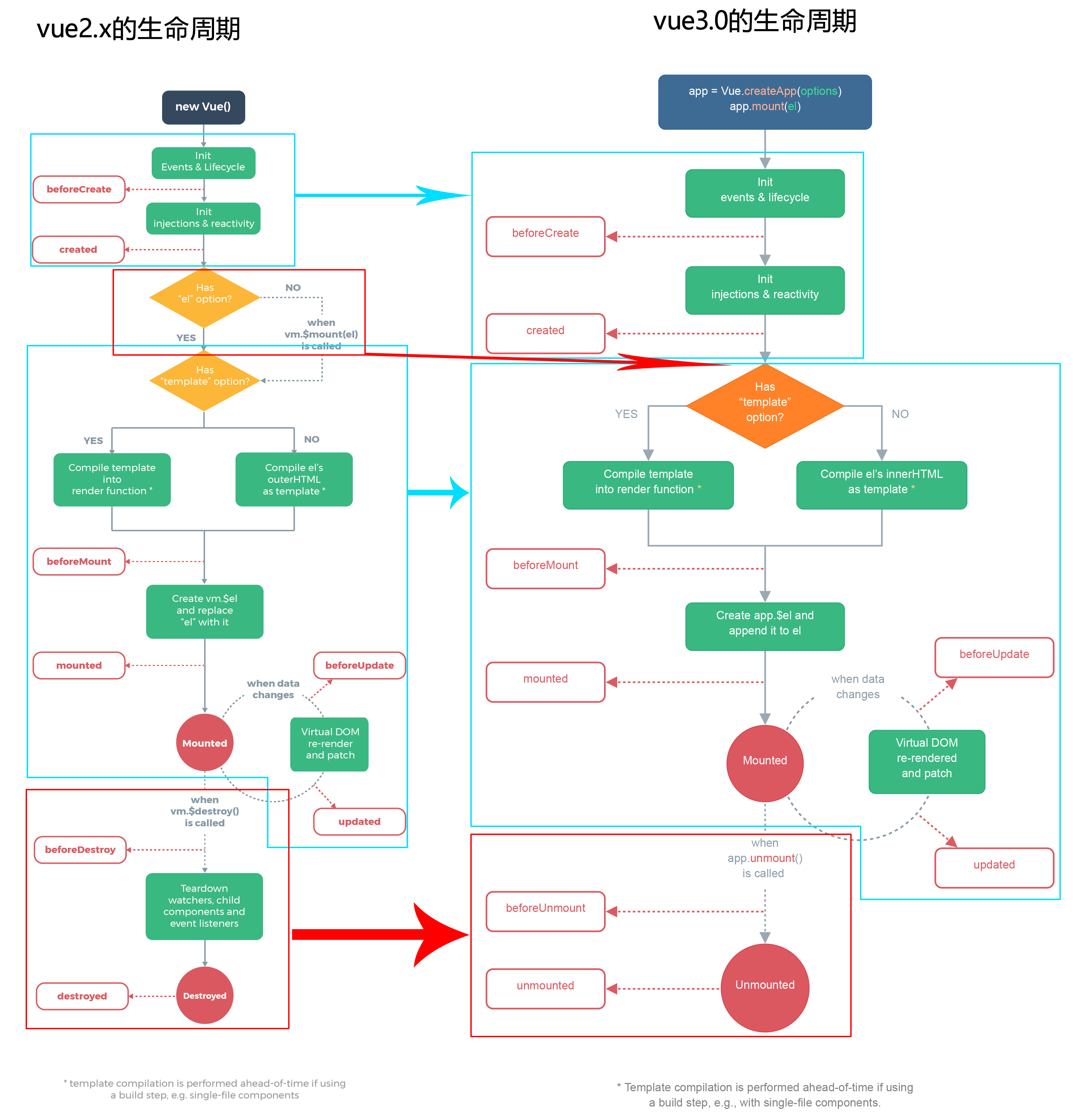
- Vue3.0 中可以继续使用 Vue2.x 中的生命周期钩子,但有有两个被更名:
beforeDestroy改名为beforeUnmountdestroyed改名为unmounted
- Vue3.0 也提供了 Composition API 形式的生命周期钩子,与 Vue2.x 中钩子对应关系如下:
beforeCreate===>setup()created=======>setup()beforeMount===>onBeforeMountmounted=======>onMountedbeforeUpdate===>onBeforeUpdateupdated=======>onUpdatedbeforeUnmount==>onBeforeUnmountunmounted=====>onUnmounted
自定义 hook 函数
- 什么是 hook?—— 本质是一个函数,把 setup 函数中使用的 Composition API 进行了封装。
- 类似于 vue2.x 中的 mixin。
- 自定义 hook 的优势: 复用代码, 让 setup 中的逻辑更清楚易懂。
toRef
- 作用:创建一个 ref 对象,其 value 值指向另一个对象中的某个属性。
- 语法:
const name = toRef(person,'name') - 应用: 要将响应式对象中的某个属性单独提供给外部使用时。
- 扩展:
toRefs与toRef功能一致,但可以批量创建多个 ref 对象,语法:toRefs(person)
其它 Composition API
shallowReactive 与 shallowRef
- shallowReactive:只处理对象最外层属性的响应式(浅响应式)。
- shallowRef:只处理基本数据类型的响应式, 不进行对象的响应式处理。
- 什么时候使用?
- 如果有一个对象数据,结构比较深, 但变化时只是外层属性变化 ===> shallowReactive。
- 如果有一个对象数据,后续功能不会修改该对象中的属性,而是生新的对象来替换 ===> shallowRef。
readonly 与 shallowReadonly
- readonly: 让一个响应式数据变为只读的(深只读)。
- shallowReadonly:让一个响应式数据变为只读的(浅只读)。
- 应用场景: 不希望数据被修改时。
toRaw 与 markRaw
- toRaw:
- 作用:将一个由
reactive生成的响应式对象转为普通对象。 - 使用场景:用于读取响应式对象对应的普通对象,对这个普通对象的所有操作,不会引起页面更新。
- 作用:将一个由
- markRaw:
- 作用:标记一个对象,使其永远不会再成为响应式对象。
- 应用场景:
- 有些值不应被设置为响应式的,例如复杂的第三方类库等。
- 当渲染具有不可变数据源的大列表时,跳过响应式转换可以提高性能。
customRef
- 作用:创建一个自定义的 ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显式控制。
- 实现防抖效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38<template>
<input type="text" v-model="keyword" />
<h3>{{ keyword }}</h3>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, customRef } from "vue";
export default {
name: "Demo",
setup() {
// let keyword = ref('hello') //使用Vue准备好的内置ref
//自定义一个myRef
function myRef(value, delay) {
let timer;
//通过customRef去实现自定义
return customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
get() {
track(); //告诉Vue这个value值是需要被“追踪”的
return value;
},
set(newValue) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
value = newValue;
trigger(); //告诉Vue去更新界面
}, delay);
},
};
});
}
let keyword = myRef("hello", 500); //使用程序员自定义的ref
return {
keyword,
};
},
};
</script>
provide 与 inject

- 作用:实现祖与后代组件间通信
- 套路:父组件有一个
provide选项来提供数据,后代组件有一个inject选项来开始使用这些数据 - 具体写法:
- 祖组件中
1
2
3
4
5
6setup(){
......
let car = reactive({name:'奔驰',price:'40万'})
provide('car',car)
......
} - 后代组件中
1
2
3
4
5
6setup(props,context){
......
const car = inject('car')
return {car}
......
}
- 祖组件中
响应式数据的判断
- isRef: 检查一个值是否为一个 ref 对象
- isReactive: 检查一个对象是否是由
reactive创建的响应式代理 - isReadonly: 检查一个对象是否是由
readonly创建的只读代理 - isProxy: 检查一个对象是否是由
reactive或者readonly方法创建的代理
Composition API 的优势
Options API 存在的问题
使用传统 OptionsAPI 中,新增或者修改一个需求,就需要分别在 data,methods,computed 里修改 。
Composition API 的优势
我们可以更加优雅的组织我们的代码,函数。让相关功能的代码更加有序的组织在一起。
Options API优化到Composition API

新的组件
Fragment
- 在 Vue2 中: 组件必须有一个根标签
- 在 Vue3 中: 组件可以没有根标签, 内部会将多个标签包含在一个 Fragment 虚拟元素中
- 好处: 减少标签层级, 减小内存占用
Teleport
- 什么是 Teleport?——
Teleport是一种能够将我们的组件 html 结构移动到指定位置的技术。
1 | <teleport to="移动位置"> |
Suspense
- 等待异步组件时渲染一些额外内容,让应用有更好的用户体验
- 使用步骤:
- 异步引入组件
1
2import { defineAsyncComponent } from "vue";
const Child = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./components/Child.vue")); - 使用
Suspense包裹组件,并配置好default与fallback1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Suspense>
<template v-slot:default>
<Child />
</template>
<template v-slot:fallback>
<h3>加载中.....</h3>
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
- 异步引入组件
其他
全局 API 的转移
Vue 2.x 有许多全局 API 和配置。
- 例如:注册全局组件、注册全局指令等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12//注册全局组件
Vue.component('MyButton', {
data: () => ({
count: 0
}),
template: '<button @click="count++">Clicked {{ count }} times.</button>'
})
//注册全局指令
Vue.directive('focus', {
inserted: el => el.focus()
}
- 例如:注册全局组件、注册全局指令等。
Vue3.0 中对这些 API 做出了调整:
- 将全局的 API,即:
Vue.xxx调整到应用实例(app)上2.x 全局 API( Vue)3.x 实例 API ( app)Vue.config.xxxx app.config.xxxx Vue.config.productionTip 移除 Vue.component app.component Vue.directive app.directive Vue.mixin app.mixin Vue.use app.use Vue.prototype app.config.globalProperties
- 将全局的 API,即:
其他改变
data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数。
过度类名的更改:
Vue2.x 写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8.v-enter,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.v-leave,
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
}Vue3.x 写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9.v-enter-from,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.v-leave-from,
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
}
移除keyCode 作为 v-on 的修饰符,同时也不再支持
config.keyCodes移除
v-on.native修饰符- 父组件中绑定事件
1
2
3
4<my-component
v-on:close="handleComponentEvent"
v-on:click="handleNativeClickEvent"
/> - 子组件中声明自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5<script>
export default {
emits: ["close"],
};
</script>
- 父组件中绑定事件
移除过滤器(filter)
过滤器虽然这看起来很方便,但它需要一个自定义语法,打破大括号内表达式是 “只是 JavaScript” 的假设,这不仅有学习成本,而且有实现成本!建议用方法调用或计算属性去替换过滤器。
……