本文为本人自学javaScript的学习笔记
什么是JavaScript 世界上最流行的脚本语言,目前来看是必学内容,学起来也很简单
严格检查模式
必须卸载js文件第一行
严格检查模式,预防js的随意性产生的问题
局部变量建议使用let定义
数据类型 变量 null 和 undefined
数 基本内容 不区分整数小数 number
1 2 3 4 5 6 123 123.4 123e3 -123 NaN Infinity
浮点数
尽量避免浮点数运算,因为有精度问题例如下面应为true,结果输出了false1 console .log((1 /3 ) === (1 -2 /3 ))
可以使用一下数学知识解决1 console .log( ( 1 /3 -(1 -2 /3 ) < 0.000000000001 ) )
字符串 用单引号(’)双引号(“) 包裹 1 2 var str1 = "hello world" var str2 = 'hello world'
转义字符 \ 1 2 3 4 5 6 'abc\'def' 'abc\rdef' 'abc\ndef' 'abc\tdef' 'abc\u4e2ddef' 'abc\x41def'
多行字符串 单反引号(`)包裹 1 2 3 var str23 = `aaa bbb ccc`
模板字符串 1 2 3 let say = "helo" let msg = `信息是:${say} ` console .log(msg)
字符串操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var str = "abcdefg" ;console .log(str.length);console .log(str[1 ]);console .log(str.toLocaleUpperCase());console .log(str.toLocaleLowerCase());console .log(str.indexOf('cde' ));console .log(str.substr(1 ,3 ));
数组
定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var arr1 = [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,'a' ,NaN ,0.1 ]var arr2 = new Array (1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,'a' ,NaN ,0.1 )console .log(arr1[2 ])arr1[2 ] = 99 console .log(arr1[2 ])console .log(arr2[3 ])console .log(arr2[10 ])
长度 1 2 3 4 5 6 var arr1 = [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,'a' ,NaN ,0.1 ]console .log(arr1)console .log(arr1.length)arr1.length = 90 console .log(arr1.length)console .log(arr1)
基本方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 var arr1 = [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,'a' ,NaN ,0.1 ]console .log(arr1.indexOf("a" ))console .log(arr1.slice(3 ))console .log(arr1.slice(3 ,5 ))console .log(arr1)arr1.push("aaa" ,"bbb" ) console .log(arr1)arr1.pop() console .log(arr1)console .log(arr1)arr1.unshift("aaa" ,"bbb" ) console .log(arr1)arr1.shift() console .log(arr1)arr1.sort() console .log(arr1)arr.reverse() console .log(arr1)var arr2 = arr.concat(["aa" ,"bb" ,"cc" ])console .log(arr1)console .log(arr2)console .log(arr1.join('-' ))
js一个数组就把动态数组,栈,队列都实现了,还是有点牛的
多维数组 1 2 3 4 var arr = [[1 ,2 ],[3 ,4 ],["5" ,"6" ]];console .log(arr)console .log(arr[1 ][1 ])console .log(arr[9 ][9 ])
对象
定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 var person = { name:"wx" , age:22 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ] } console .log(person)console .log(person.name)console .log(person.age)console .log(person.tags[2 ])console .log(person.hhh)
动态添加删减属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var person = { name:"wx" , age:22 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ] } console .log(person)delete person.nameconsole .log(person)person.new_name = 'wx1' console .log(person)
常用方法
判断属性值是否存在对象中 xxx in xxx1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var person = { name:"wx" , age:22 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ] } console .log('name' in person)console .log('toString' in person)
判断属性是否为自身拥有的hasOwnProperty1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var person = { name:"wx" , age:22 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ] } console .log(person.hasOwnProperty('toString' ))console .log(person.hasOwnProperty('name' ))
布尔值 逻辑运算 比较运算符 1 2 3 var a = 1 "1" == 1 "1" === 1
NaN === NaN 与所有的数值都不相等 包括自己
只能通过isNaN(NaN)判断是否为NaN
流程控制 判断 if else
完全参考java1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var flag = 10 if (flag > 5 ) { console .log(">5" ) } else if (flag > 8 ) { console .log(">8" ) } else { console .log("<=5" ) }
循环
while1 2 3 4 5 var i = 1 ;while (i < 100 ) { i += 1 console .log(i) }
do while1 2 3 4 do { console .log(i) i += 1 } while (i < 100 )
for1 2 3 for (let i = 0 ; i <= 100 ; i++) { console .log(i) }
数组循环1 2 3 4 5 var arr1 = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 'a' , NaN , 0.1 ]for (let value in arr1){ console .log(arr1[value]) }
forEach 循环1 2 3 4 var arr1 = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 'a' , NaN , 0.1 ]arr1.forEach(function (value ) console .log(value) })
Map & Set Map 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 'use strict' var map = new Map ([["a" ,100 ],["b" ,90 ],["c" ,80 ]]);var value = map.get("b" );console .log(value);console .log(Array .from(map));map.set("d" ,70 ) console .log(map.get("d" ));console .log(Array .from(map));map.delete("d" ); console .log(map.get("d" ))console .log(Array .from(map));
Set 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 'use strict' var set = new Set ([1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,56 ,1 ,7 ,7 ,8 ]);console .log(Array .from(set));set.add("1" ) console .log(Array .from(set));set.delete(1 ) console .log(Array .from(set));console .log(set.has(1 ));
iterator(es6) 迭代器 数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var arr1 = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 'a' , NaN , 0.1 ]for (let value in arr1){ console .log(value) } for (let value of arr1){ console .log(value) }
迭代器 Map 1 2 3 4 var map = new Map ([["a" ,100 ],["b" ,90 ],["c" ,80 ]]);for (let x of map){ console .log(x) }
迭代器 Set 1 2 3 4 var set = new Set ([1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 'a' , NaN , 0.1 ]);for (let x of set){ console .log(x) }
函数 定义 方法1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 function abs (x ) if (x > 0 ) { return x; } else { return -x; } } console .log(abs(-10 ));console .log(abs(10 ));console .log(abs());
方法2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 var abs = function (x ) if (x > 0 ) { return x; } else { return -x; } } console .log(abs(-10 ));console .log(abs(10 ));console .log(abs());
匿名函数,但可以把结果赋值给abs ,通过abs就可以调用
调用 参数为空则 返回 undefined 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var abs = function (x ) if (x > 0 ) { return x; } else { return -x; } } console .log(abs(-10 ));console .log(abs(-10 , 9 ));console .log(abs(10 ));console .log(abs());
javascript 可以传入任意个参数,
arguments代表传入的所有的参数,表示一个数组,1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 var test = function (x ) console .log("x->" + x) if (arguments .length > 1 ) { for (var i = 0 ; i < arguments .length; i++) { console .log(arguments [i] + "\n" ) } } return 1 ; } console .log(test(-10 ));console .log(test(-10 , 10 , 111 , 121 , 4343 ));console .log(test(10 ));console .log(test());
arguments包含所有参数,但调用者只希望使用除了当前参数之后的所有多余参数进行附加操作,如何进行操作?1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 var test = function (x,y,...rest ) console .log("x->" + x+",y->" + y) console .log(rest) return 1 ; } console .log(test(1 ,2 ));console .log(test(1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,6 ));console .log(test(10 ));console .log(test());
变量作用域 作用域测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 'use strict' var test = function (x ) var x = 1 } console .log(x)
用var生命的拥有作用域
在函数体内声明则不可以在本函数体外使用
非要实现在函数外调用则可以使用闭包
内部函数作用域测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 var test = function (x ) var a = 1 var test1 = function (y ) var b = 2 console .log(a) console .log(b) } test1(1 ); }
内部函数可访问外部函数的成员,反之则不行
内部外部函数,成员同名的话,则从内向外查找
自动提升变量声明 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var test = function (x ) var a = "1" + b; console .log(a) var b = "2" ; } var test = function (x ) var b; var a = "1" + b; console .log(a) b = "2" ; }
所以 写一个脚本,需要一开始统一定义(规范)
全部先定义后使用
全局变量 1 2 3 4 5 6 var x = 1 ;function f ( console .log(x); } console .log(x);f();
全局对象 window 1 2 3 var x = 1 ;alert(x) alert(window .x)
默认拥有全局变量,默认绑定在window对象下面(window 就代表浏览器)
alert()函数本身也是window的一个变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var x = 1 ;window .alert(x)var myalert = window .alert;myalert('自定义' ); window .alert = function (message ) } window .alert('alert失效' )window .alert = myalert;window .alert('恢复' )
解决全局变量冲突(规范)
因为所有的全局变量都会绑定到 window,如果不同的js文件使用了相同的全局变量,则会产生冲突,任何减少冲突?
避免重名
不适用,因为大型网站js很多,很难保证自己的 命名唯一
把自己的代码放在自己定义的唯一名称空间中
(参考jquery)1 2 3 4 5 var myVar = {};myVar.name = "wx" ; myVar.age = "20" ; myVar.fun = function (a, b )
局部作用域
常量(只读变量)
全部大写命名的变量为常量(规范,但未强制,非常危险)1 2 3 4 5 var PI = '3.14' ;console .log(PI);PI = '111111' ; console .log(PI);
ES6引入常量关键字(const)1 2 3 4 const PI = '3.14' ;console .log(PI);PI = '111111111' ; console .log(PI);
方法 定义
方法就是把函数放在对象里面1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 var person = { name:"wx" , birth:1998 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ], age: function ( var myage = new Date ().getUTCFullYear(); return myage - this .birth; } } console .log(person.age())
调用方法必须带()
this 介绍及使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function getAge ( var myage = new Date ().getUTCFullYear(); return myage - this .birth; } var person = { name:"wx" , birth:1998 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ], age: getAge } console .log(person.age())console .log(getAge())
apply()
apply函数所指定的对象,在js中可以控制this的 指向1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function getAge ( var myage = new Date ().getUTCFullYear(); return myage - this .birth; } var person = { name:"wx" , birth:1998 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ], age: getAge } var age = getAge.apply(person,[])console .log(age)
内部对象
标准对象1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 typeof 123 "number" typeof "123" "string" typeof '123' "string" typeof true "boolean" typeof NaN "number" typeof {}"object" typeof []"object" typeof Math .abs"function" typeof undefined "undefined"
Date 日期类型 使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 var data = new Date ();console .log(data)console .log(data.getFullYear()); console .log(data.getMonth()); console .log(data.getDate()); console .log(data.getDay()); console .log(data.getHours()); console .log(data.getMinutes()); console .log(data.getSeconds()); console .log(data.getTime() + "" ); console .log(data.getUTCFullYear())
转换 1 2 var data = new Date (1622327479772 );console .log(data)
JSON
在javaScript中一切对象均可以用Json表示
对象{}
数组[]
键值对 key: value
对象转化为Json字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var person = { name:"wx" , age:22 , tags:[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ] } console .log(person)console .log(JSON .stringify(person))
Json字符串转化为对象 1 2 var person = JSON .parse('{"age":22,"name":"wx","tags":{"0":1,"1":2,"2":3,"3":4,"4":5,"5":6,"length":6}}' );console .log(person)
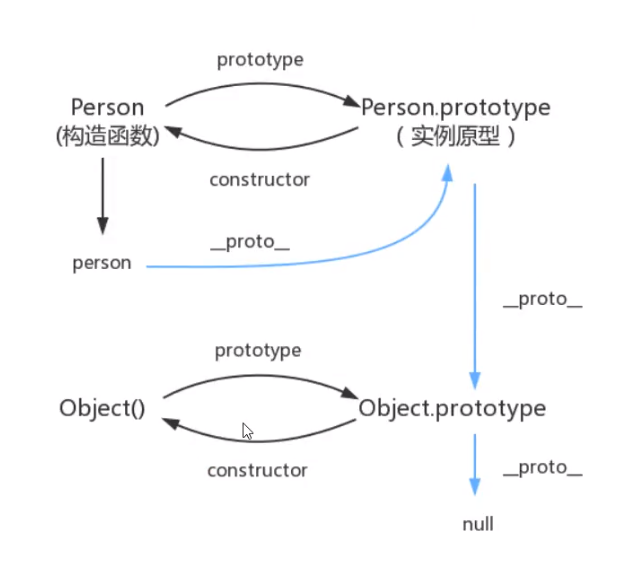
面向对象编程 指向原型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 var person = { name: "aaaa" , birth: 1998 , tags: [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ], age: function ( var myage = new Date ().getUTCFullYear(); return myage - this .birth; } } var me = { name: "wx" } me.__proto__ = person; console .log(me.age());
person1.__proto__ = person;是指向原型的意思,也就是java父类
class继承 定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class person constructor (props ) super (props); this .props = props; } hello ( alert(this .props + "say hello" ) } } var me = new person("wx" );me.hello();
class 继承 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class person constructor (name ) super (name); this .name = name; } hello ( alert(this .name + "say hello" ) } } class student extends person constructor (name,age ) super (name); this .name = name; } studentHello ( alert(this .name + " student say hello" ) } } var me = new person("wx" );me.studentHello();
原型链 操作BOM对象 JavaScript的诞生就是为了能让人们在浏览器中运行脚本
window
代表浏览器窗口1 2 3 4 5 6 window .innerHeightwindow .innerWidthwindow .outerHeightwindow .outerWidth
navigator
navigator封装了浏览器的信息1 2 3 4 window .navigator.appNamewindow .navigator.appVersionwindow .navigator.userAgentwindow .navigator.platform
screen
代表屏幕1 2 window .screen.widthwindow .screen.height
location
location 代表当前页面url信息1 2 3 4 5 6 window .location.hrefwindow .location.hostwindow .location.protocolwindow .location.reload()
document
代表当前页面、html、dom文档树1 2 3 4 5 6 document .titlevar dl = window .document.getElementById("" );window .document.cookie
history
代表历史记录(不建议使用)1 2 3 4 window .history.back()window .history.forward()
操作Dom对象
Dom:文档对象模型
整个浏览器网页就是个树形结构
更新:Dom
遍历:Dom节点 得到Dom节点
删除:删除一个Dom节点
添加:添加一个Dom节点
获得Dom节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <div id ="father" > <h1 > 标题1</h1 > <p id ="p1" > p1</p > <p class ="p2" > p2</p > </div > <script > var h1 = document .getElementsByTagName("h1" ); var p1 = document .getElementById("p1" ); var p2 = document .getElementsByClassName("p2" ); var father = document .getElementById("father" ); var childrens = father.children; </script > </body > </html >
更新Dom节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <div id ="id1" > <h1 > 标题1</h1 > <p id ="p1" > p1</p > <p class ="p2" > p2</p > </div > <script > var id1 = document .getElementById("id1" ); id1.innerText = "文本改变" ; id1.innerHTML = "<strong > 加粗超文本</strong > " id1.style.color = "red" ; id1.style.fontSize = '200px' ; </script > </body > </html >
删除Dom节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <div id ="father" > <h1 > 标题1</h1 > <p id ="p1" > p1</p > <p class ="p2" > p2</p > </div > <script > var father = document .getElementById("father" ); var p1 = document .getElementById("p1" ); father.removeChild(p1); var p1 = document .getElementById("p1" ); var father = p1.parentElement; father.removeChild(p1); father.removeChild(father.children[1]) </script > </body > </html >
插入Dom节点 已存在的节点插入 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <strong id ="new_text" > 新增的文本</strong > <div id ="list" > <p1 > P1</p1 > </div > <script > var text = document .getElementById('new_text' ); var list = document .getElementById("list" ); list.appendChild(text); </script > </body > </html >
创建新标签插入 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <p id ="p" > p</p > <div id ="list" > <p1 > P1</p1 > <p2 > P2</p2 > </div > <script > var myList = document .getElementById("list" ); var new_text = document .createElement('p' ); new_text.id = 'nwp' ; new_text.innerText = '新增p节点1' ; list.appendChild(new_text); var p = document .getElementById('p' ); var p2 = document .getElementsByTagName('p2' )[0 ]; myList.insertBefore(p,p2); </script > </body > </html >
c插入标签扩展 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <div id ="list" > <p1 > P1</p1 > </div > <script > var list = document .getElementById("list" ); var myScript = document .createElement('script' ); myScript.setAttribute('type' ,'text/javaScript' ); list.appendChild(myScript); var myStyle = document .createElement('style' ); myStyle.setAttribute('type' ,'text/css' ); myStyle.innerText = 'body{ background-color:chartreuse}' ; var head = document .getElementsByTagName('head' )[0 ]; head.appendChild(myStyle); </script > </body > </html >
操作表单 获取/操作 表单的值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <form action ="post" > <p > <span > 用户名</span > <input type ="text" id ="username" > </p > <p > <span > 性别</span > <input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="1" id = 'boy' checked =checked > 男 <span > 性别</span > <input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="0" id = 'girl' > 女 </p > </form > <script > var uName = document .getElementById('username' ); console .log(uName.value); uName.value = '123' ; console .log(uName.value); var uSex_boy = document .getElementById('boy' ); var uSex_girl = document .getElementById('girl' ); console .log(uSex_boy.value); console .log(uSex_girl.value); console .log(uSex_boy.checked); console .log(uSex_girl.checked); uSex_girl.checked = true ; </script > </body > </html >
提交表单 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > </head > <body > <form action ="post" > <p > <span > 用户名</span > <input type ="text" id ="username" name ="username" > </p > <p > <span > 密码</span > <input type ="text" id ="password" name ="input-password" > </p > <p > <button type ="submit" onclick ="text()" > </button > </p > </form > <script > function test ( var username= document .getElementById('username' ); var password = document .getElementById('input-password' ); console .log(username.value + ":" password.value); console .log(password.value + ":" password.value); password.value = md5(password.value); console .log(username.value + ":" password.value); return true ; } </script > <script src ="https://cdn.bootcss.com/blueimp-md5/2.10.0/js/md5.min.js" > </script > </body > </html >
jQuery
文档
https://jquery.com/ https://jquery.cuishifeng.cn/
获取
https://www.jq22.com/cdn/ <script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-migrate-1.2.1.min.js"></script><script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
选择器示例
规则
$(selector).action()
示例1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > <script src ="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js" > </script > </head > <body > <a href ="" id ="test" > 111</a > <script > document .getElementById('test' ); $('#test' ).click(function ( alert('test' ); }) </script > </body > </html >
action示例
规则
$(selector).action()
示例1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > <script src ="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js" > </script > <style > #divMove{ width : 500px ; height : 500px ; border : 1px solid red ; } </style > </head > <body > <span id ="mouseMove" > :</span > <div id ="divMove" > 在此移动 </div > <script > $(function ( $('#divMove' ).mousemove(function (e ) $("#mouseMove" ).text(e.pageX + ", " + e.pageY); }); }); </script > </body > </html >
操作Dom 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > title</title > <script src ="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js" > </script > </head > <body > <ul id = 'test-ul' > <li name ="l1" > l1</li > <li name ="l2" > l2</li > <li name ="l3" > l3</li > <li name ="l4" > l4</li > </ul > <script > var l1 = $('#test-ul li[name = l1]' ).text(); console .log(l1) $('#test-ul li[name = l1]' ).text('12121' ); $('#test-ul li[name = l1]' ).css('color' ,'red' ); $('#test-ul li[name = l2]' ).show(); $('#test-ul li[name = l2]' ).hide(); </script > </body > </html >
技巧
笔记到此就结束了